Question
Question: If a,b,c, and d are the smallest positive angles in ascending order of magnitude which have their si...
If a,b,c, and d are the smallest positive angles in ascending order of magnitude which have their sines equal to the positive quantity k, then prove that 4sin(2a)+3sin(2b) + 2sin(2c)+sin(2d)=21+k.
Solution
First we will let the sines of a,b,c and d to be k and the write each angle in terms of the sin of a and put all the values in the given equation to get the value of k.
sin(2π−x)=cosx sin(π+x)=−sinx sin(23π−x)=−cosxComplete step by step solution:
The given equation is:
4sin(2a)+3sin(2b) + 2sin(2c)+sin(2d)=21+k................(1)
Since sines of all the angles is equal therefore,
Let sina=sinb−sinc=sind=k
Since a,b ,c and d are in ascending order therefore a is the smallest angle.
Also, since all the angles are positive angles implies the sines of these angles are also positive
And since we know sin is positive only in first and second quadrants.
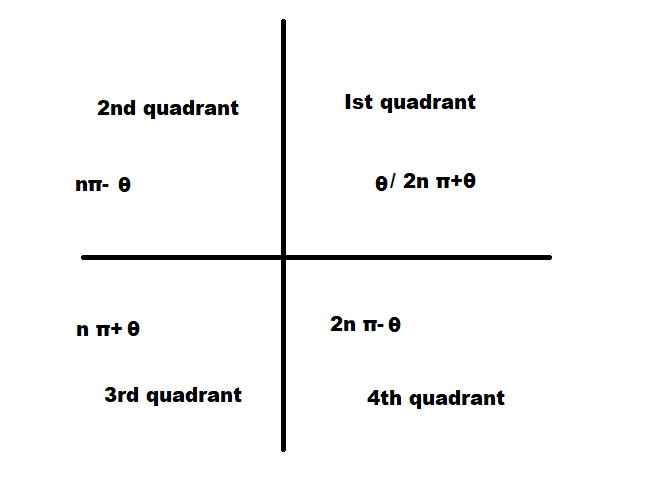
Hence, each angle can be written in terms of angle a :
b=π−a
Then, half of angle b is:
2b=2π−2a
Similarly,
Now putting these values in Left hand side of equation1 we get:
LHS=4sin(2a)+3sin(2b) + 2sin(2c)+sin(2d) LHS=4sin(2a)+3sin(2π−2a) + 2sin(π+2a)+sin(23π−2a)Now we know that,
sin(2π−x)=cosx sin(π+x)=−sinx sin(23π−x)=−cosxApplying these formulas in the above equation we get:
LHS=4sin(2a)+3cos(2a)−2sin(2a)−cos(2a) LHS=2sin(2a)+2cos(2a) LHS=2[sin(2a)+cos(2a)] LHS=2[(sin(2a)+cos(2a))2]Now applying the following formula:
(a+b)2=a2+b2+2ab
We get:
LHS=2[sin2(2a)+cos2(2a)+2sin(2a)cos(2a)]
Now applying following formulas:
We get:
LHS=2[1+sin(2×2a)] LHS=2[1+sin(a)]Now since therefore,
LHS=21+k
And also, RHS=21+k
Therefore, LHS=RHS
Hence proved.
Note:
Since the angles, a,b,c, and d are in ascending order and the values of sines of these angles are equal, therefore, the values of these angles are to be taken in symmetry of sinusoidal graph such that the sines of the angles are positive.
