Question
Question: If \[0 < x < 1\] ,then \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \ri...
If 0<x<1 ,then \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} =
A) 1+x2x
B) x
C) x1+x2
D) 1+x2
Solution
In this question, we have to find the value given expression. We proceed by considering, the inverse term y=cot−1x and solve it to find the value of y=sin−11+x21 and y=cos−11+x2x. Now we put this value in the expression and simplify to find the required answer. We will also use the fact that cos(cos−1θ)=θ and sin(sin−1θ)=θ where θ is the angle.
Complete step by step answer:
This question is based on the inverse trigonometric function.
Consider the given question,
We have to find the value of \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}
Let us consider the inverse trigonometric ratio y=cot−1x,
now taking inverse , we have
This implies , x=coty
Now we find the value of siny and cosy
i.e. siny=1+x21 and cosy=1+x2x.
Taking inverse in both the values we get
y=sin−11+x21 and y=cos−11+x2x
Thus, we have y=cot−1x=sin−11+x21=cos−11+x2x
Thus from the given question, we have,
\Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}
Putting the value from above, we have
\Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right)} \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}
We know that cos(cos−1θ)=θ and sin(sin−1θ)=θ,
Hence we have,
\Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {x\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }} + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}
Taking LCM inside the curly bracket, we get
\Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {\dfrac{{{x^2} + 1}}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}
By cancelling on dividing 1+x2 by 1+x2, we have
\Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} } \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}
On squaring we have,
⇒1+x2[1+x2−1]21
On simplifying we have,
⇒1+x2[x2]21
Hence on simplifying we have,
⇒x1+x2
Hence, \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} = x\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} . So, option C is correct.
Note:
To find the value of inverse trigonometric ratio when value of one of the trigonometric ratio is given , we proceed as follow:
For example , we find the value of inverse other inverse trigonometric ratio , when we are given θ=cot−1x
This imply x=cotθ
We know that cotθ=perpendicularbase
Now from the right angle triangle , we have
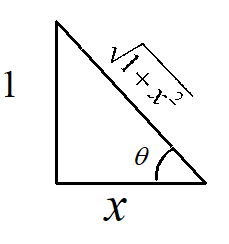
From Pythagoras theorem we have
hypotenuse=1+x2
Hence, sinθ=1+x21
Taking the inverse of the values we get .
Hence , θ=sin−11+x21 .
Similarly we can find the value of other inverse trigonometric ratios.
