Question
Question: Identify Z in the following series \({C_2}{H_5}OH\xrightarrow{{PB{r_3}}}X\xrightarrow{{alc.KOH}}Y\xr...
Identify Z in the following series C2H5OHPBr3Xalc.KOHYdil.H2SO4Z
(A)CH2=CH2
(B)CH3CH2OH
(C)CH3−CH2−O−CH2−CH3
(D)None
Solution
In these types of questions, we need to know step by step the product formed after the reaction in the presence of a catalyst. If we need to find the compound of Z, first we need to know the products formed at X and Y.
Complete answer:
First we see the product formed after the reaction between ethanol and PBr3. This reaction proceeds in two steps. In the first step the alcohol is converted into a good leaving group by forming a bond to P( O−P bonds are very strong) and displacing Br from P, this is essentially a nucleophilic substitution at phosphorus.
Now that the oxygen has converted to a good leaving group, a substitution reaction at carbon can occur. The bromide ion that is displaced from phosphorus attacks carbon via a backside attack, forming C−Br and left with a new ethyl bromide. So, the X is C2H5Br.
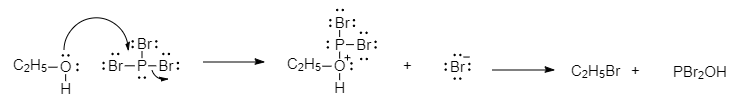
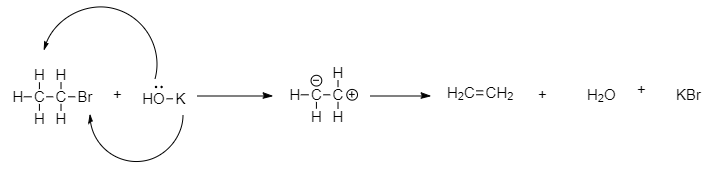
Now, ethyl bromide undergoes reaction in the presence of alcohol KOH, forming ethane. When ethyl bromide is boiled with KOH, the hydrogen atom transfers its electron pair to the adjacent carbon bond, and bromide is removed from the molecule. This forms a double bond between the alpha and beta carbon atoms and gives ethane as a product. So. The Y is CH2=CH2.
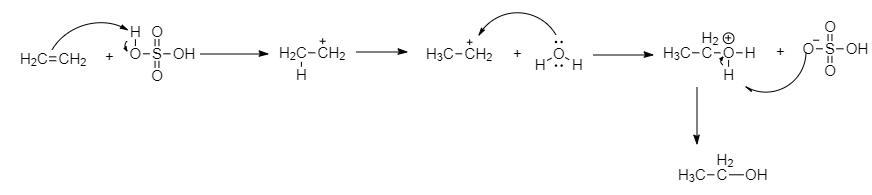
When ethane reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, it forms ethanol. All alkenes react with dilute sulphuric acid and give alcohol. This is a hydration reaction. A water molecule is added through double bonds and may give primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol. So the element Z, we get ethanol.
Therefore the correct answer is option B.
Note:
When haloalkane with β- hydrogen atoms are boiled with an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, they undergo the elimination of hydrogen halide (HX) resulting in the formation of alkenes.. The dilute sulphuric acid acts as a catalyst in hydrolysis of alkene.
