Question
Question: Identify the structure of propanoic anhydride. (A) \( {\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\...
Identify the structure of propanoic anhydride.
(A) (CH3CH2CO)2O
(B) (CH3CO)2O
(C) (CH3CH2CH2CO)2O
(D) CH3COOCOCH2CH3
Solution
An acid anhydride is a functional derivative of carboxylic acid. In organic chemistry, an acid anhydride contains the functional group R(CO)O(CO)R’ where R and R’ are two alkyl groups.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When carboxylic acids are heated in the presence of a strong dehydrating agent such as phosphorus pentoxide or concentrated sulphuric acid, acid anhydrides are formed by the elimination of a molecule of water from two molecules of the acid. For example, ethanoic anhydride is obtained by the treatment of two molecules of ethanoic acid in presence of phosphorus pentoxide or concentrated sulphuric acid.
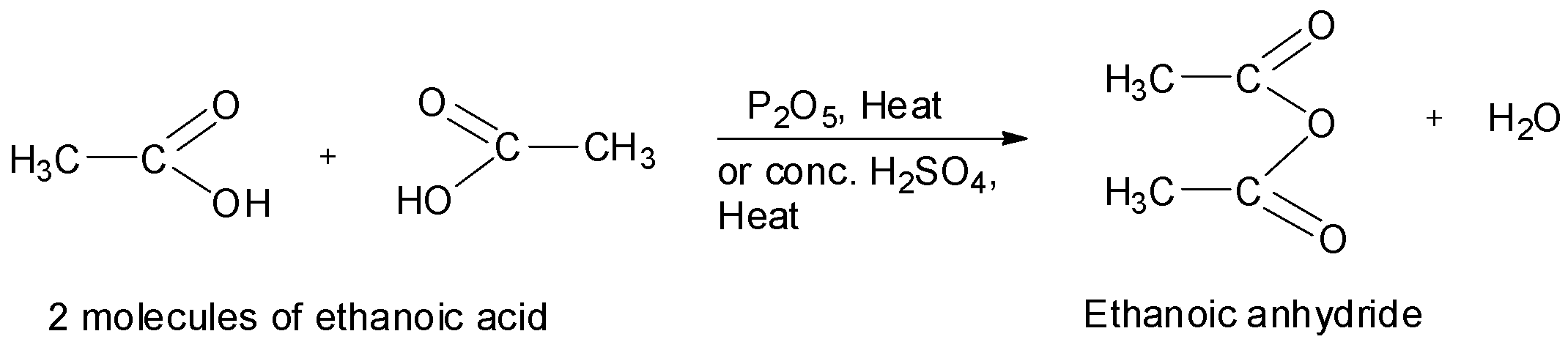
Similarly, propanoic anhydride can be prepared from propanoic acid. Now, the structure of propanoic acid is as shown below.
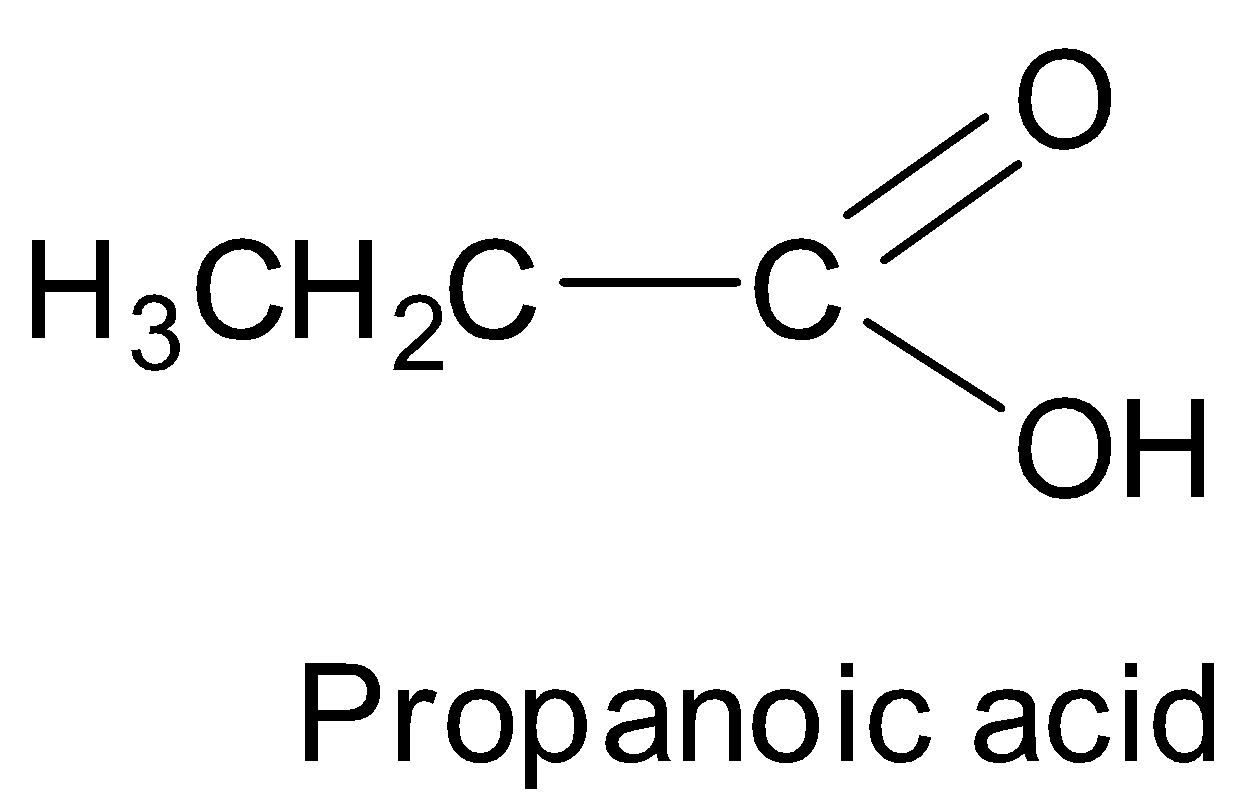
We can see that propanoic acid has 3 carbon atoms.
Thus, propanoic anhydride will be obtained when two molecules of propanoic acid is heated with phosphorus pentoxide or concentrated sulphuric acid.
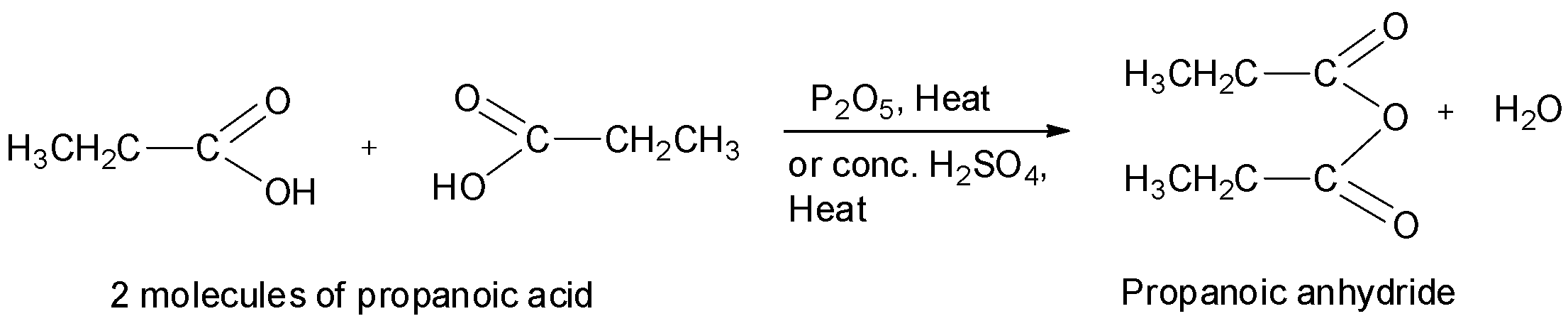
Thus, we can see that propanoic acid has the structure:
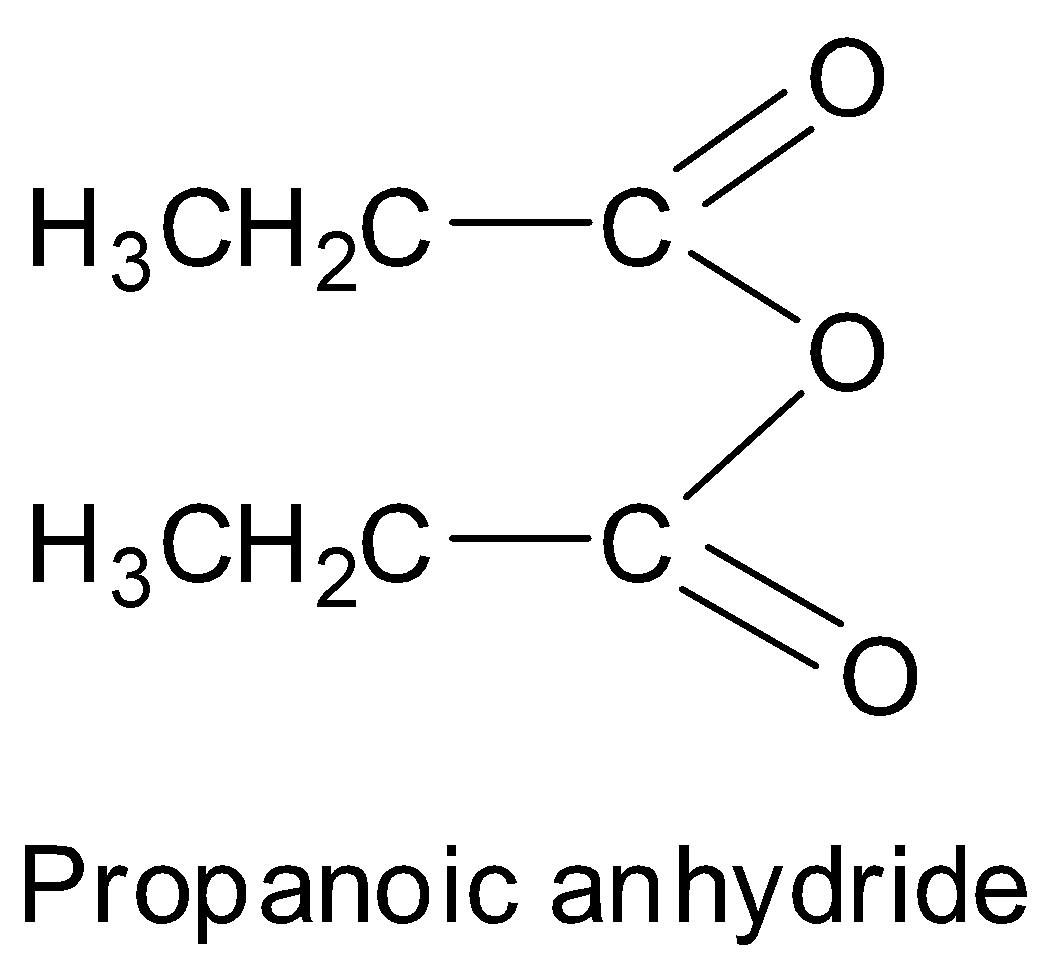
This can also be written in the form of formula as CH3CH2COOCOCH2CH3 or (CH3CH2CO)2O . Hence, option A is correct.
Option B is incorrect as (CH3CO)2O is ethanoic anhydride. Option C is incorrect as (CH3CH2CH2CO)2O is butanoic anhydride. Option D is incorrect as CH3COOCOCH2CH3 is ethanoic propanoic anhydride.
Note:
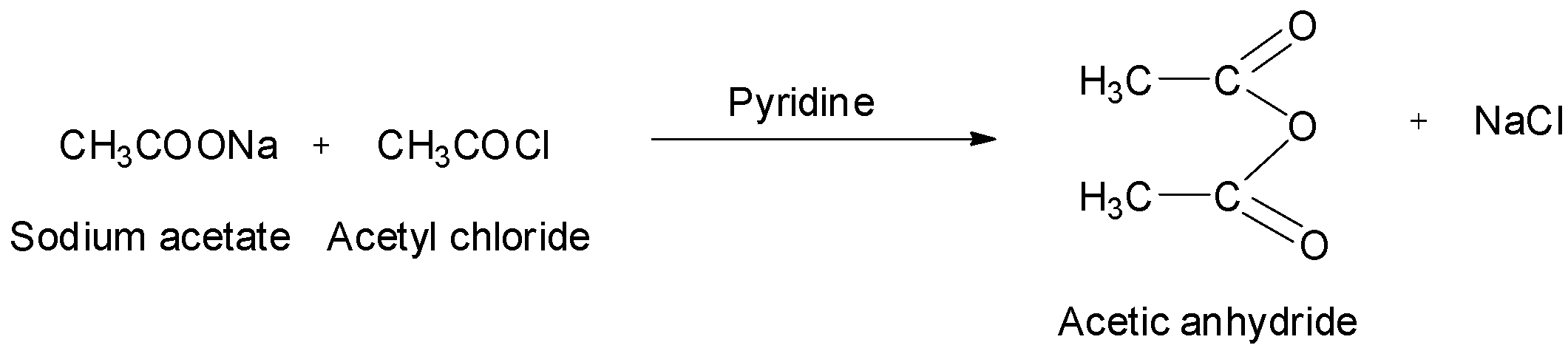
Acetic anhydrides can also be obtained by treating acid chlorides with carboxylic acids in the presence of pyridine as a base. The reaction is shown below.
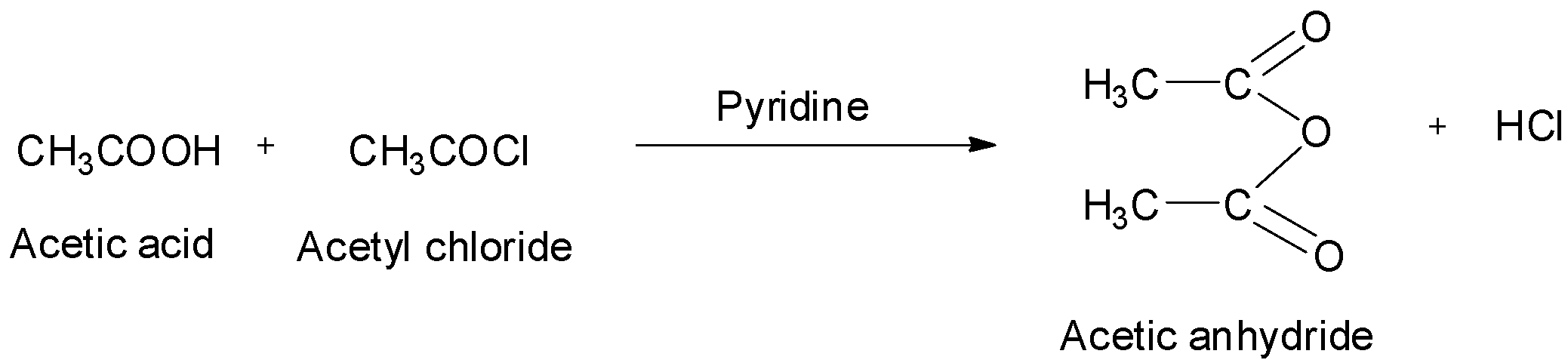
They can also be obtained by treating acid chlorides with sodium salts of carboxylic acids. The reaction is: