Question
Question: Identify the product of the given condensation reaction:- 
(A)
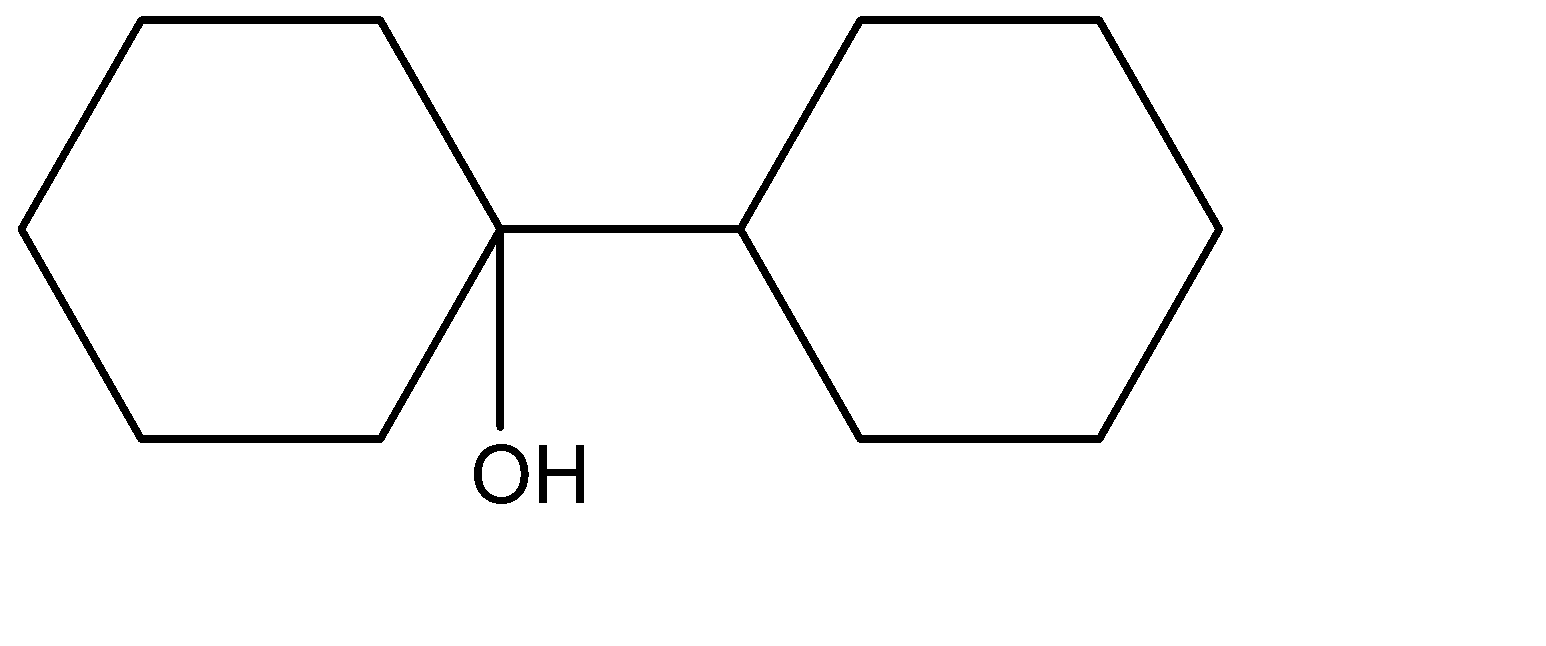
(B)
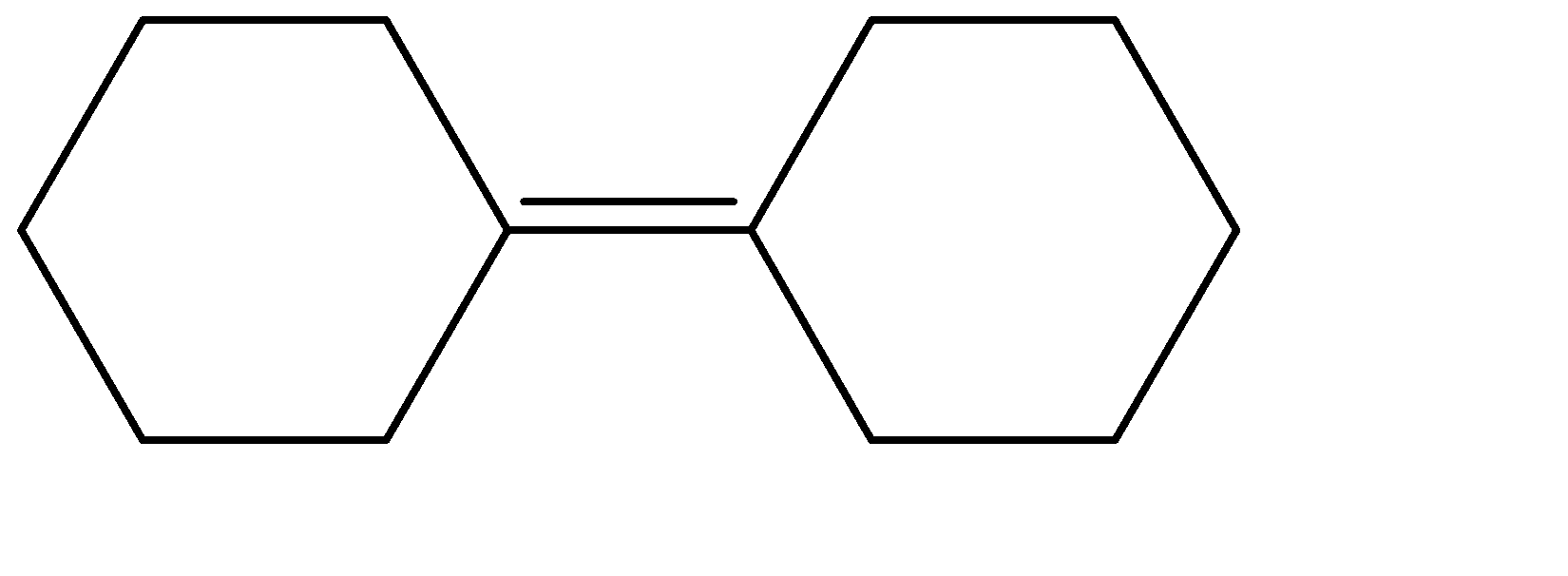
(C)
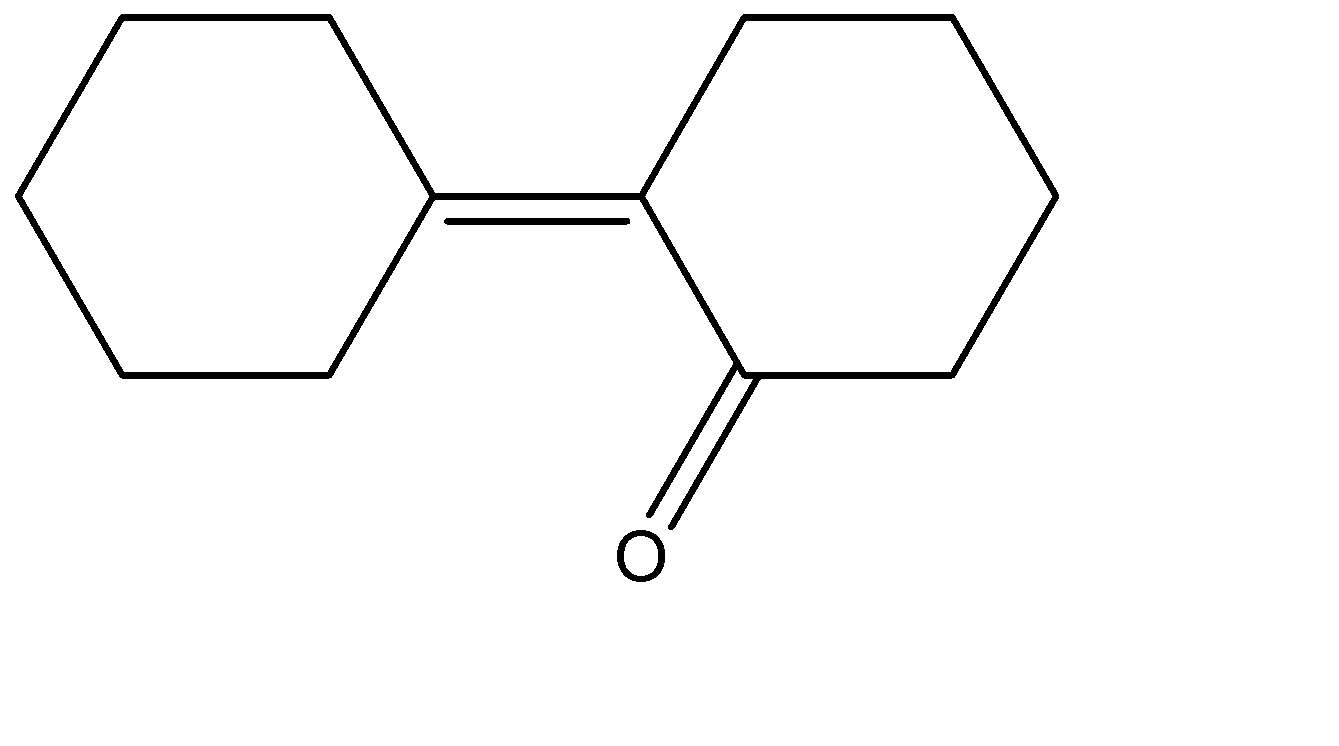
(D)
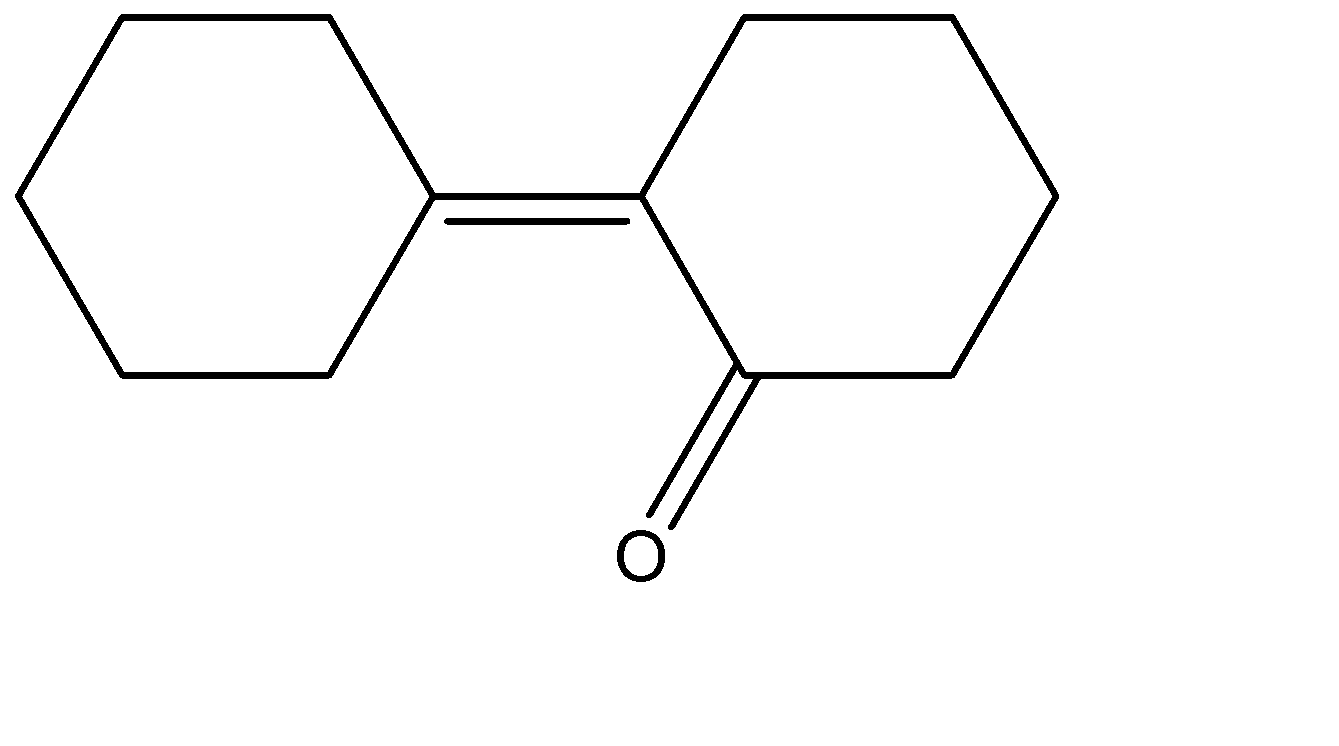
Solution
As we know that a condensation reaction is the combination of two molecules or compounds to form a single molecule where usually is the loss of a small molecule such as water. However other molecules can also be lost in condensation processes such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide based on the work up process or the substituents attached to the reactant.
Complete answer:
Since the reactant provided for the condensation reaction is a ketone, it is most probably an aldol condensation reaction. So let us study about it:-
Aldol condensation occurs in aldehydes and ketones having α−hydrogen with a dilute base to give aldols (also known asβ−hydroxy aldehyde/ketone).
-If the condensation reaction occurs between two same carbonyl compounds then it is known as a self-condensation reaction but if the reaction occurs between two different carbonyl compounds then it is called crossed aldol condensation.
-Formation of enolate ion:-
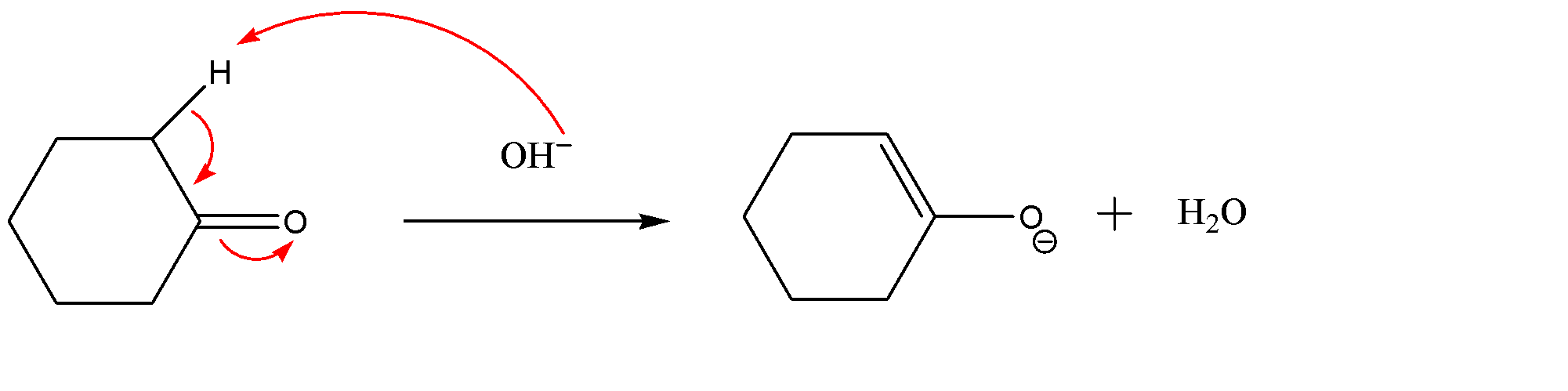
As we can see that the hydroxide ion (OH−) will attack acidic hydrogen adjacent to the carbonyl group due to which the electron cloud would transfer to oxygen atom. This way the formation of enolate ions takes place.
-Attack on another molecule containing carbonyl group:-
After the formation of enolate ion, it will act as a nucleophile and attack the electrophilic part of the other carbonyl compound. Since only one type of ketone molecules are present, it is a self-aldol condensation reaction.
-Work up by H2O:-
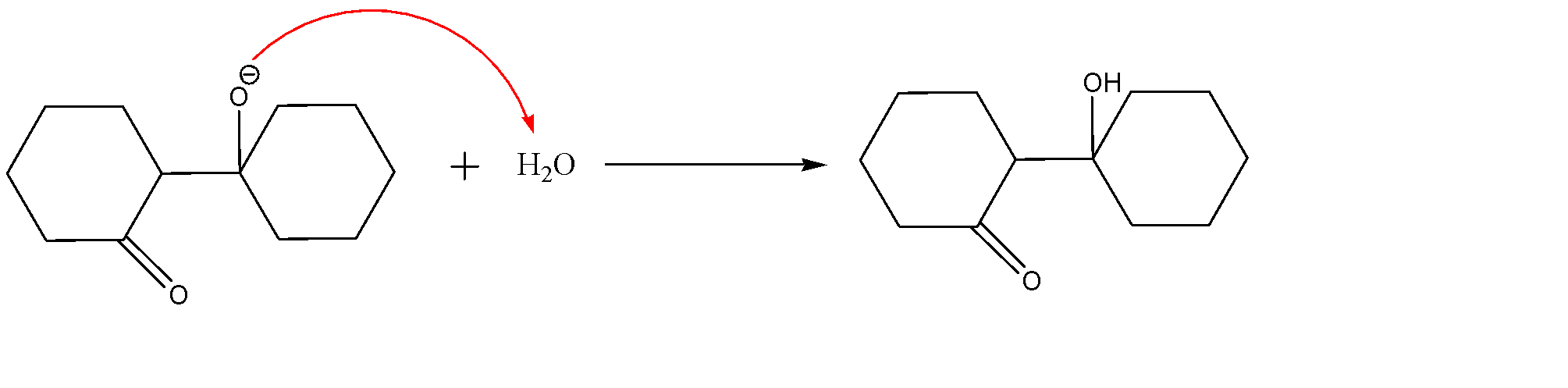
The formation of water molecules in the first step will act as a work-up molecule and will lead to the formation of β−hydroxy ketone.
-Condensation:-
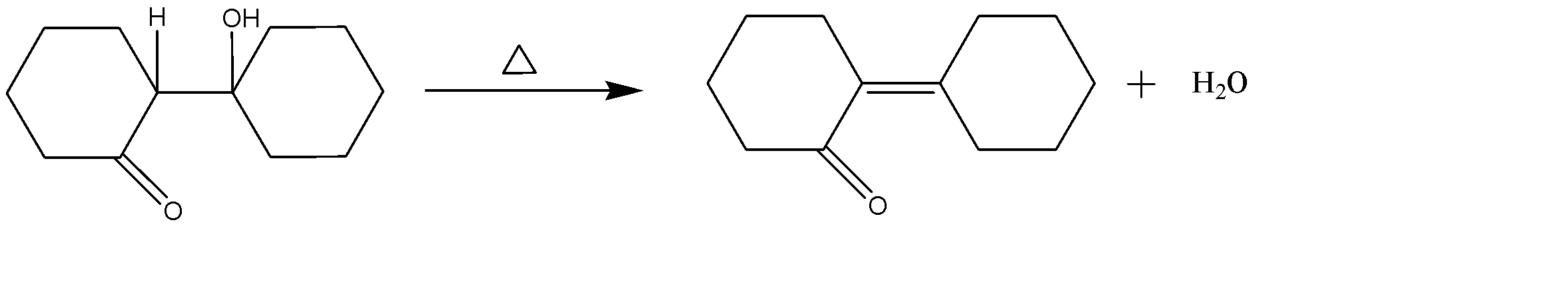
Since the reaction is being heated, and α−H is present adjacent to the alcohol group, therefore dehydration of β−hydroxy ketonewill occur and a water molecule is released with the desired product.
Hence the correct answer is option (C) .
Note:
-When hydroxide ion concentration is low, then the formation of enolate ion is slow and it becomes the rate determining step but when hydroxide ion concentration is high then attack of enolate ion on other aldehyde or ketone groups becomes the rate determining step.
-Condensation (elimination of water molecule) will only occur when α−H is present adjacent to the alcohol group.
