Question
Question: Identify the product of Cummene-peroxide reaction among the following : A. Phenol+acetaldehyde B...
Identify the product of Cummene-peroxide reaction among the following :
A. Phenol+acetaldehyde
B. phenol+acetone
C. ethanol+acetaldehyde
D. ethanol+acetone
Solution
When cummene is oxidized in presence of oxygen, it forms cummene peroxide which is not stable. So it breaks down into 2 different compounds on hydrolysis to increase the stability and energy is released in this reaction. So, cummene peroxide is an intermediate and gives different compounds on hydrolysis.
Complete step by step solution:
-The structure of cummene is represented as
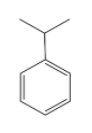
When it is oxidized, it forms cummene peroxide. The cummene radical is formed due to oxidation by the removal of tertiary benzylic hydrogen. This radical is then attacked by the oxygen atom to form the peroxide. The reaction can be shown as
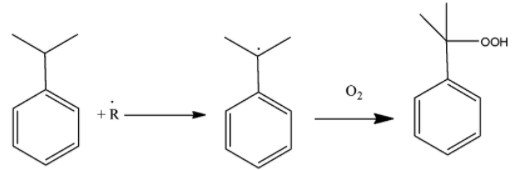
-This compound is very unstable. It is yellowish in colour and so can be distinguished easily. It is unstable and this makes the compound work as a reaction intermediate. Intermediates are the compounds which are formed instantaneously and they disappear soon because they react with other compounds or decompose themselves.
-Cummene is easily formed when benzene undergoes Friedel-Craft alkylation along with propylene. It has tertiary hydrogen present in it which is reactive and is removed on oxidation. That position is occupied by oxygen molecules to form peroxide which makes the compound intermediate.
-The terminal peroxide group will be protonated in acidic medium and when hydrolysis of the cummene peroxide is done, then the products formed are phenol and acetone. The process is called Hock rearrangement. Mechanism is similar to the hydroboration oxidation process.
-The complete reaction can be shown as
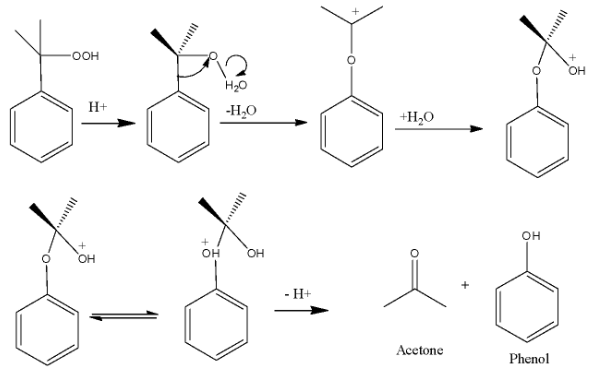
Thus we see that the products formed are phenol and acetone and the correct option is B.
-To check the mechanism of the reaction, we see that first protonation occurs which makes water molecules leave from the peroxide bond leading to the formation of carbocation. This carbocation is hydrolysed and ultimately forms the desired products.
So, we can say that the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Cummene hydrogen peroxide acts as a good oxidizing agent and is slightly soluble in water. Since it is an organic compound, it is readily soluble in esters, acetone and alcohols due to formation of hydrogen bond present due to –OH bond.
