Question
Question: Identify the functional group present in acetic acid: A. 
B.
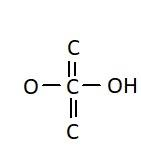
C.
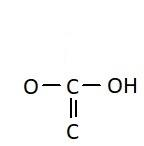
D.
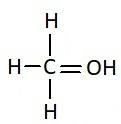
Solution
Before identifying the functional group in acetic acid, let’s find out what a functional group is. Functional groups are the atoms or groups or molecules which decide the reactivity of the molecules to which they are attached.
Complete step by step answer:
Sometimes, certain elements can also be considered as functional groups. Few examples are oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur etc. Alkanes are generally unreactive when compared to other functional groups. Thus they are not considered as functional groups. But alkenes are considered as functional groups. Alkenes are compounds which are represented as C=C. Similarly, each functional group has their own symbols like alcohols have −OH group, ethers have −O etc. Alcohols have a suffix “ol” at the end of the chemical name.
Similarly, the chemical names having “acid” as suffix are generally carboxylic acids. They have a carboxyl group attached to it. Carboxylic groups are involved in the carbonyl compounds. Carbonyl means they have a carbon atom which is double bonded to oxygen atom. Carboxylic groups have a carbonyl group, −C=O and a hydroxyl group, −OH. Thus they have two oxygen atoms, i.e. one from carbonyl and one from hydroxyl group. The hydroxyl group and carbonyl group is attached to the same carbon. Moreover, the carboxylic group usually comes at the end of the carbon chain. They are also known as alkanoic acid. The term “oic acid” is used for naming the carboxylic acids. “Acetic” is generally used for compounds having two carbon atoms. Thus the chemical formula of acetic acid is CH3COOH. Thus the functional group in acetic acid is represented as:
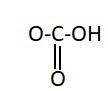
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: The functional groups in each type of organic compounds are specific. They have a major role in formation of DNA, proteins, etc. Such functional groups involve hydroxyl −OH, methyl −CH3, amino −NH2, carboxyl −COOH etc.
