Question
Question: Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following co...
Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following compounds:
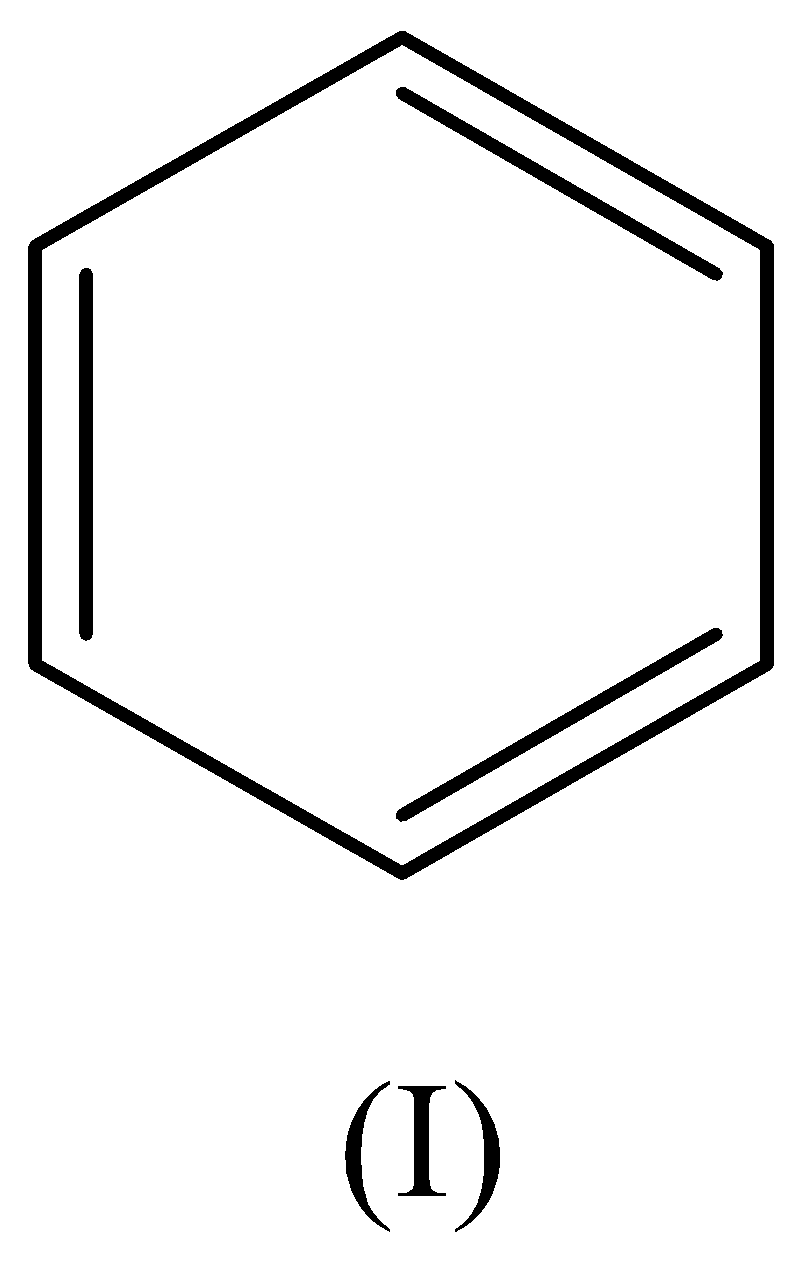
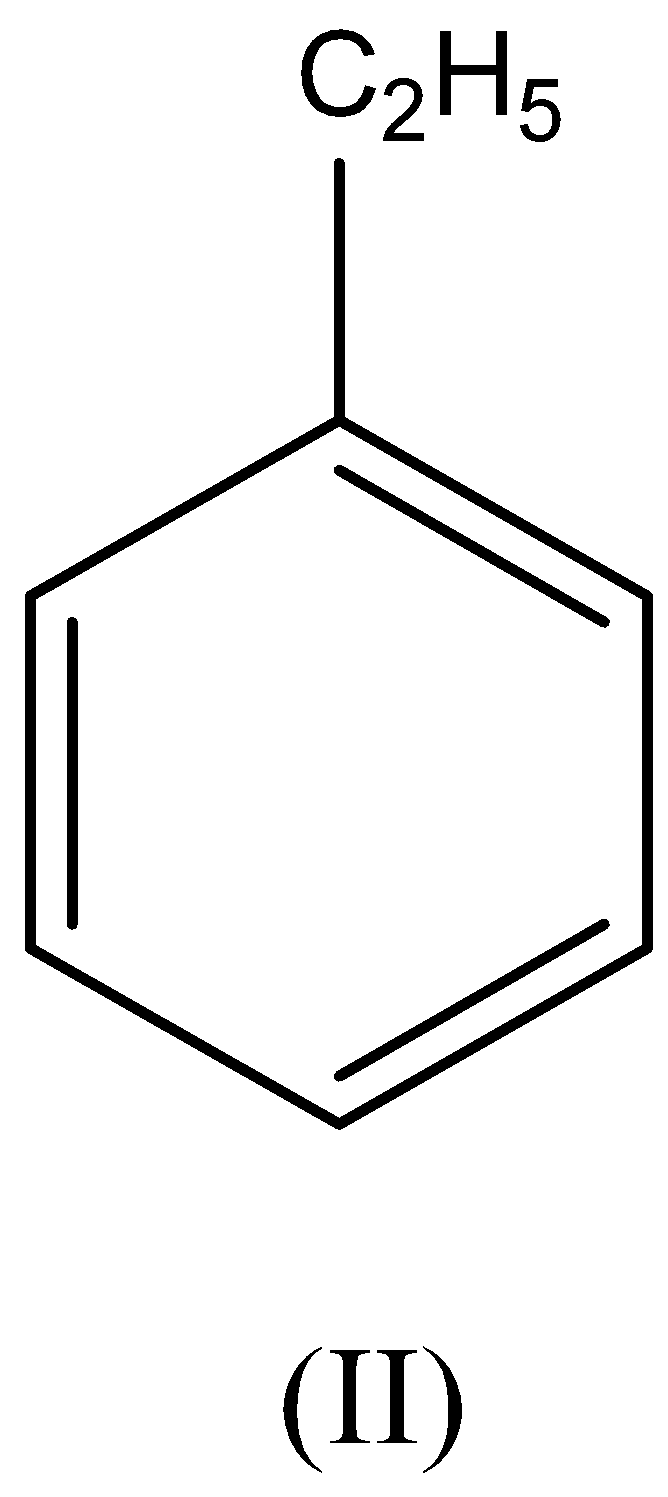
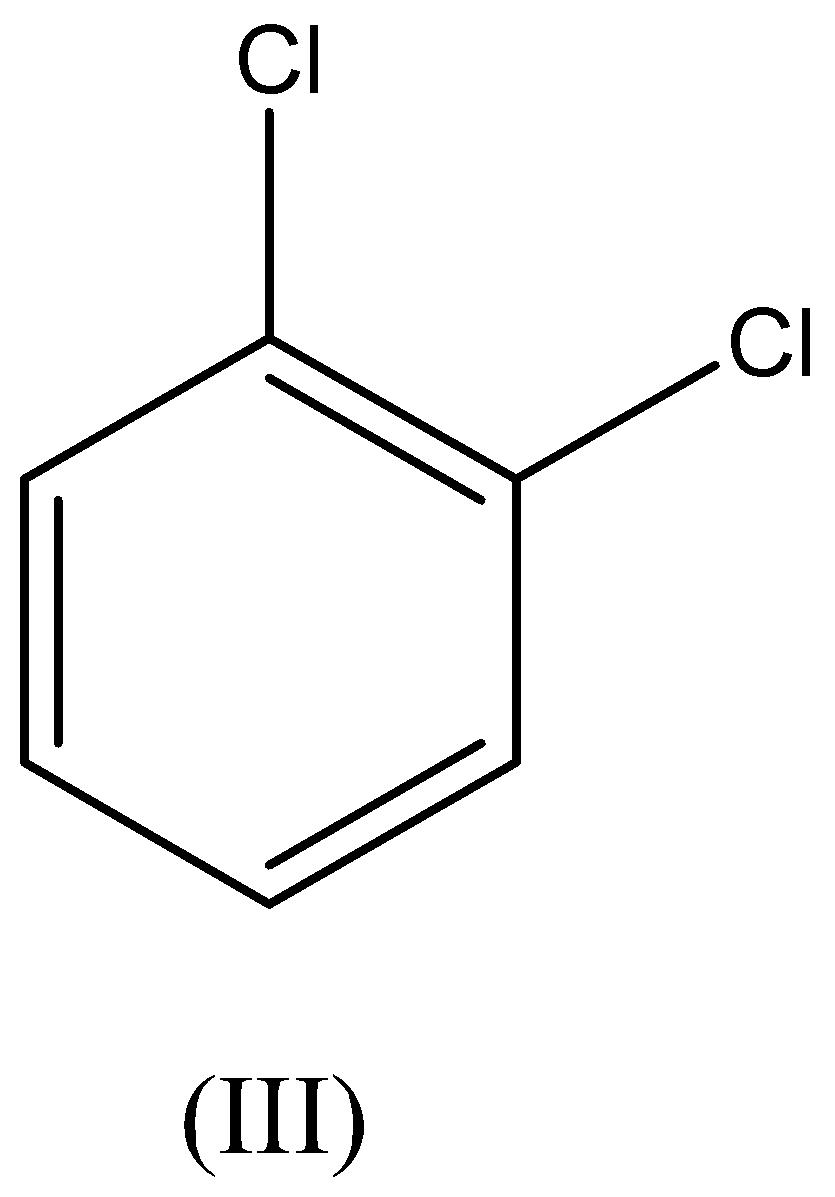
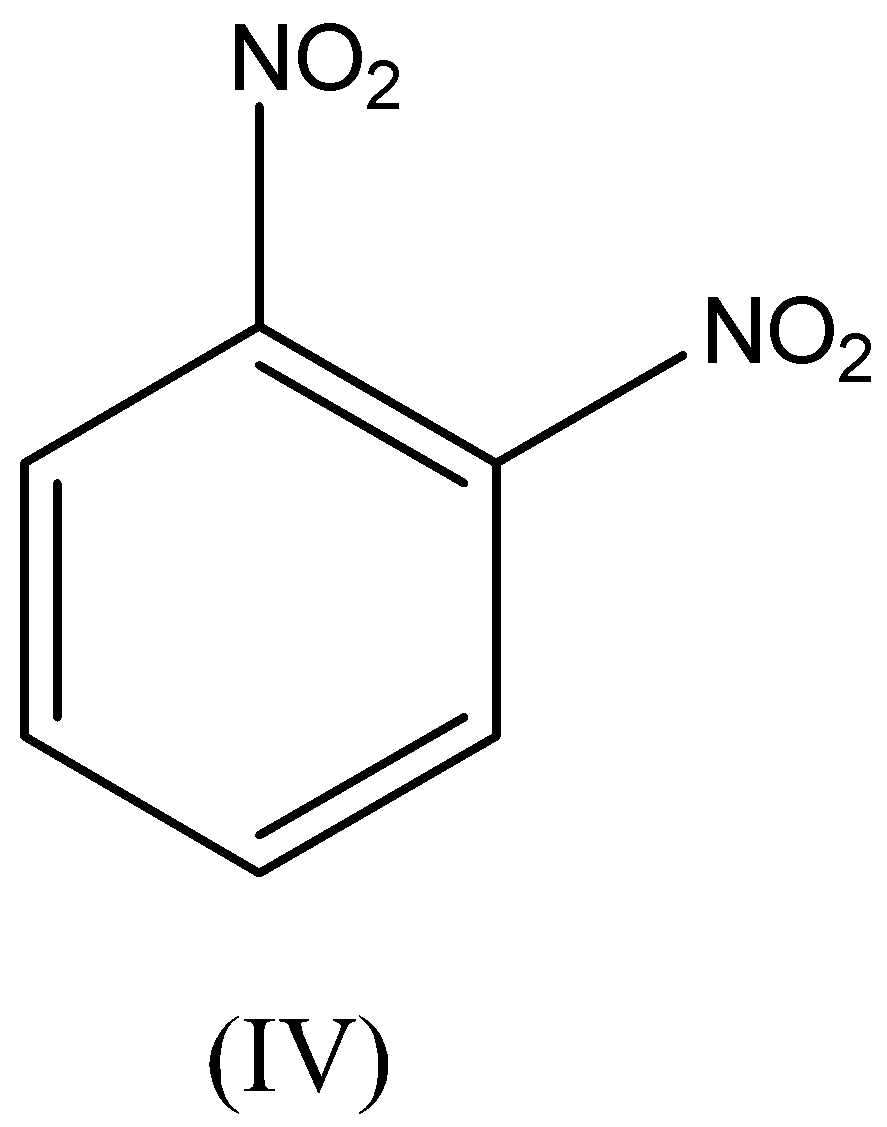
A. I>II>III>IV
B. IV>III>II>I
C. II>I>III>IV
D. II>III>I>IV
Solution
In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, the bonding atom is replaced by an electrophile. Electrophiles are atoms and molecules which have strong affinity to electron donating atoms or molecules. The reactivity is more at para and ortho position. To determine the order of reactivity, we need to check the reactivity and R and I effect of groups present in each compound.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that the electron releasing groups are an atom or functional group which donates electrons towards the conjugated system leading to form resonance. Examples: alkyl groups, -OH, -OR, ….
We have to know that the electron donating groups attract the electron form the conjugated system which leads to make the ring deactivate. Examples: halogens, aldehyde, ketone, ester, carboxylic acid etc..
In the above given compounds, the functional groups present are ethyl group, chlorine and nitro.
We have to remember that the ethyl group is an electron releasing group which gives an electron pair toward the benzene ring thus leads to the ethyl benzene being more reactive than benzene.
We have to remember that the chloro and nitro groups are electron withdrawing in nature which gains the electron from the benzene ring which leads to the electrophilic substitution getting deactivated towards the benzene ring. Therefore, the reactivity of chloro and nitro groups is less than the benzene.
We have to remember that the chloro group is highly reactive than the nitro group. Therefore, the ortho dinitrobenzene is less reactive than the ortho chloro benzene.
Now we can arrange the compounds based on the order of reactivity as,
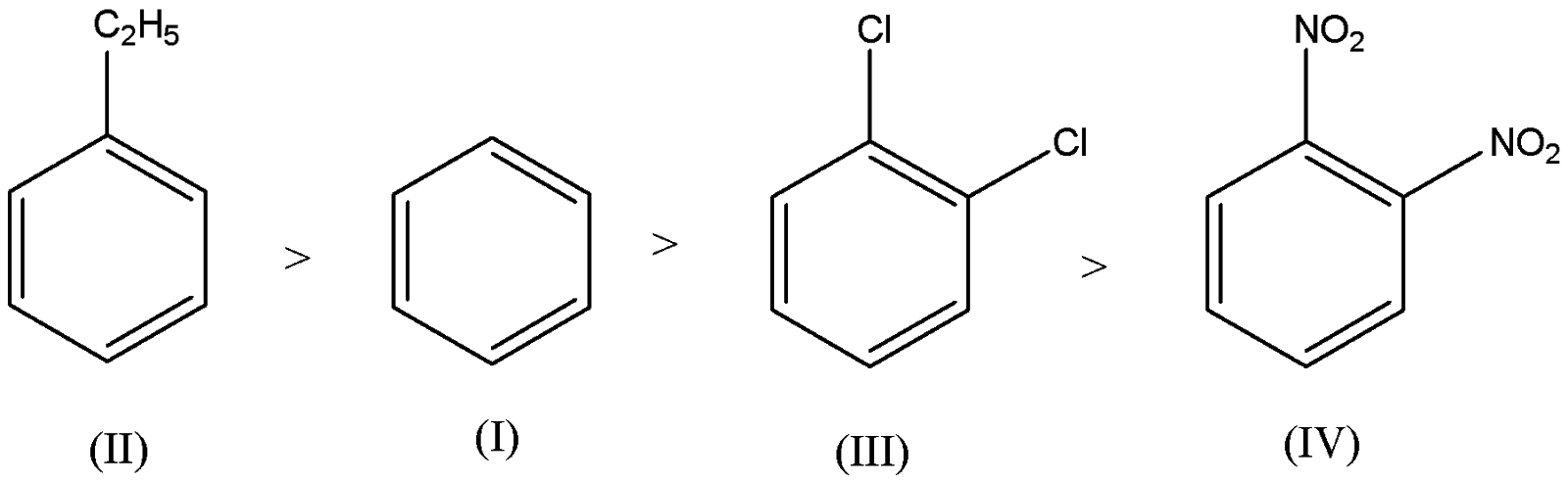
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: We have to know that the electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions exhibit substation of weak electron donation atoms with an electrophile. In the order of reactivity, the activating groups due to high I and R effect acts as electron donating groups which is preferable for the reaction. While deactivating groups due to weak I and R effect act as electron withdrawing groups making it less reactive.
