Question
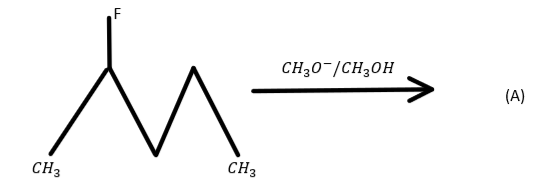
Question: Identify the compound (A) in the reaction:  in the reaction:
A.
B.
C.
D.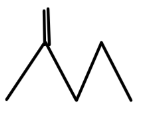
Solution
We know that when haloalkanes react with CH3O− dissolved in ethanol then they form alkenes. And which alkene will form is decided by the number of hydrogen atoms at the adjacent carbon atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first talk about the term alkenes, alkanes and alkynes.
Alkanes have the general formula as CnH(2n+2), where n is the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon. Alkenes have the general formula as CnH(2n), where n is the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon. And similarly alkynes have the general formula as CnH(2n−2), where n is the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon.
Halo-alkanes: They are defined as the alkanes in which one hydrogen atom is replaced by one halogen atom i.e. fluorine, chlorine, iodine, etc.
Now we know that when haloalkanes react with CH3O− dissolved in ethanol then they form alkenes. And which alkene will form is decided by the number of hydrogen atoms at the adjacent carbon atoms. And which alkene will form is decided by the number of hydrogen atoms at the adjacent carbon atoms. The alkene which will have the largest number of hydrogen atoms at the adjacent carbon atom will form in large quantity and other will also produce but in small quantity. So in the question the reaction of 2−fluoro pentane with CH3O− dissolved in ethanol is given. So the product formed will be CH3CH = CHCH2CH3 because in this compounds number of hydrogen atoms attached to the adjacent carbon is high i.e. 5.
In option A number of hydrogen atoms attached to the adjacent carbon is 3.
In option B the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the adjacent carbon is 2.
In option B the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the adjacent carbon is 5. But in this number of carbon atoms are greater than the number of carbon atoms in the reactants. So it is wrong.
So, option C is correct.
Note: Isomerism: This is defined as the phenomenon in which more than one compounds have the same chemical formula but they have different chemical structures.
Structural isomerism: They are defined as the compounds which differ in the connectivity between the atoms that constitute the compound d.
Stereoisomerism: The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangements of atoms in three-dimensional structure.
