Question
Question: Ice is trapped by a metal gauze at the bottom of a tube containing water. The water is heated strong...
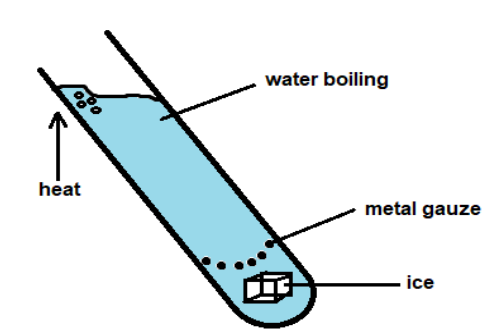
Ice is trapped by a metal gauze at the bottom of a tube containing water. The water is heated strongly at the top, but the ice only melts very slowly. Why does the ice melt so slowly?
A. Heat energy always travels upwards
B. Hot water is more dense than cold water
C. Metal gauze does not allow heat to pass through
D. Water is a poor conductor of heat
Solution
As shown in the figure, ice is placed at the bottom of a tube containing water. The ice is trapped by a metal gauze at the bottom of the tube. The top of the water is heated and the ice at the bottom melts slowly. We have to find the reason for the slow melting of the ice.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that water transfers heat through convection. Convection is the process where heated molecules of water move up and cold water molecules present at the bottom of the tube move down and get heated. Since the water is heated at the top of the tube, the heated molecules will not travel down. Hence the only way for the heat at the top of the tube to travel down is through conduction. Water is not good at conducting heat. Hence the ice will be melting slowly.
Therefore, the reason why ice melts slowly is that heat energy always travels upwards.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Additional Information:
Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct heat. The ability of heat conductivity differs in different materials. Copper, silver, and gold have the highest thermal conductivity.
Note: The method through which heat travels in solids is called conduction. In conduction, the movement of molecules is not needed unlike in convection. Thermal conduction is different from electrical conduction. Since electrons are good conductors of heat and electricity metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
