Question
Question: (i) Write the IUPAC name of the complex. \(\left[\mathrm{Cr}\left(\mathrm{NH}_{3}\right)_{4} \mathrm...
(i) Write the IUPAC name of the complex. [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cl
(ii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(en)3]3+?(en=ethane-1,2- diamine)
(iii) why is [NiCl4]2 paramagnetic but [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic? (Cr=24,Co=27,Ni=28)?
Solution
In order to solve the questions we are going to follow the IUPAC guidelines to write the name and electronic configuration to find the type of isomerism and magnetic behaviour of the compound.
Complete step by step solution
i. In order to write the name of the compound first of all we will write the elements present, and the elements are chromium (Cr), Nitrogen(N), Hydrogen (H), Chlorine (Cl).Here in this compound chromium is having 4 electron valency , hence it forms a compound [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cland , it has made bonds with 3 amino acid, 3 chlorides to form a compound and its IUPAC name is Tetraamminedichlorochromium(III) chloride.
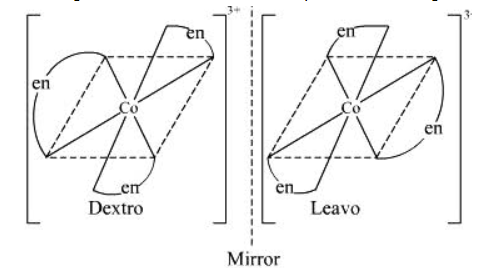
ii. The complex compound [Co(en)3]3+ that is called en=ethane-1,2-diamine shows optical isomerism. In optical isomerism the compounds have same atoms and same bonds, only difference is that they have different orientation, hence when placed together they look as a mirror image to each other but cannot be superimposed. Similarly in above compound also optical isomerism occurs, you can see the diagram below and check that they look mirror images:-
iii. In [NiCl4]2 Ni have two unpaired valence electrons in its d-subshell, also Ni has oxidation of +2, and the chlorine present in the compound has weak ligand field and the unpaired electrons works against Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity resulting in paramagnetic character of the compound. Whereas in [Ni(CO)4] carbonyl has a strong ligand field which in turn aligns the free electrons, resulting in working in favour of Hund’s maximum multiplicity. Therefore the compound shows diamagnetic character.
Note:
Students will make mistakes in structural drawing of the optical isomers. They will also make errors while determining the effect of ligand field on the magnetic characteristics of the compound.
