Question
Question: (i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex: \({[Co{(N{H_3})_5}Cl]^{2 + }}\) (ii) Wri...
(i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex:
[Co(NH3)5Cl]2+
(ii) Write the formula for the following complex:
Potassium tetrachloronickelate (II)
Solution
To know the IUPAC name of a compound we need to break the compound in parts called parent chain and substituents and name them. Then combining the substituents we get the IUPAC name.
Complete step by step answer:
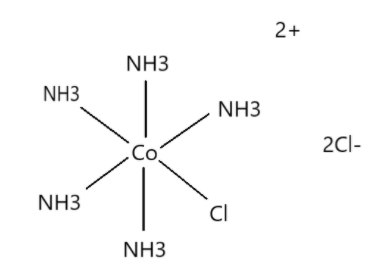
i. The IUPAC name of the compound is Penta ammine chloride cobalt (III) dichloride. It is also called Chloropentaamminecobalt chloride. It is a chloride salt which is red-violet in colour, diamagnetic and water soluble salt. This compound is of academic and historical interest.
According to IUPAC naming, pentaammine means five amine groups that are attached to the central cobalt atom. Chloro prefix is used due to the presence of chlorine atom and cobalt name is used because of its presence in the compound. The two chlorine atoms due to which +2 charge is there on the compound, the name dichloride is used. This is how this compound is named. The structure of the compound is as given below.
ii. Potassium tetrachloronickelate (II) has chemical formula K2[Ni(Cl)4] . Here tetra means four and tetrachloro means four atoms of chlorine with nickel atoms at the centre. Potassium atoms are connected to the centre nickel atom. It is a blue colour metal complex. This colour is due to tetrachloronickelate ion which was first observed in 1944 when Remy and Meyer melted caesium chloride and caesium nickel trichloride together.
Additional Information:
There are various IUPAC rules for naming organic compounds. The base part of the name reflects the number of carbons in the parent chain. The suffix of the name reflects the type of functional group present on the parent chain. Other groups which are attached to the parent chain are called substituents.
Note:
IUPAC naming rules are different for compounds with different suffixes and prefixes to identify them. Alcohols, alkanes, alkyl halides, Alkenes and alkynes, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters and amines are different categories with different prefixes and suffixes to identify them.
