Question
Question: (i) What is the role of Sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber? (ii) Identify the monomers in the ...
(i) What is the role of Sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber?
(ii) Identify the monomers in the given polymer.
(iii) Arrange the following polymers in the decreasing order of their intermolecular forces: Terylene, Polythene, Neoprene. 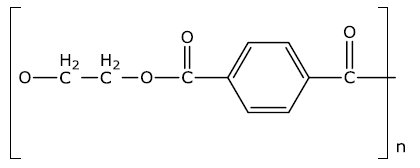
Solution
Hint: Mineral sulfur is generally utilized for fixing the shape of cross-joins between the elastic chains in the vulcanization procedure. During intensifying, a high versatile state of sulfur at temperatures somewhere in the range of 40°C and 70°C stretches off its particles and then breaks off these flimsy and powerless needles into pieces.
Complete answer:
Vulcanization is a compound procedure that changes over common elastic and other poldine elastomers into cross-connected polymers. The most widely recognized vulcanization operator is sulfur. Its structure spans between singular polymer atoms when warmed with elastic. Frequently an impetus and initiator are added to quicken the vulcanization procedure. The cross-connected elastomers have significantly better mechanical properties. The unvulgarized elastic has poor mechanical properties and isn't truly tough.
The monomer of the given compound is as follow:
Hexamethylenediamine - H2N(CH2)6NH2 and Adipic Acid -COOH(CH2)4COOH
Decreasing order of the intermolecular forces:
Terylene > Polythene > Neoprene.
A Monomer is an iota or little particle that may tie artificially to different monomers to shape a Polymer (implies numerous parts). A Polymer is characterized as an enormous particle made out of rehashing auxiliary units.
NOTE : Monomers bind together to give shape to the polymers during a mixed response is called Polymerization, where the two particles connect together by sharing electrons.
Intermolecular Forces are the powers which act at the nuclear level. These powers keep the particles and atoms bound together. Without these powers no atom would be an acceptor. These Forces make connections between atoms, including powers among atoms and different kinds of neighboring particles.
E.g.- Atoms or particles, Hydrogen holding.
