Question
Question: Hyper conjugation is: A. \(\sigma - \pi \) conjugation B.Delocalization of \(\sigma \) and \(\pi...
Hyper conjugation is:
A. σ−π conjugation
B.Delocalization of σ and π bond
C.No bond resonance
D.All of the above
Solution
Basically, hyper conjugation is a permanent effect in which the localization of sigma electrons of C-H bond of an alkyl group is directly attached to an atom of the unsaturated system. Further, it stabilizes the carbocation as it helps in the dispersal of positive charges.
Complete step by step answer:
Hyper conjugation refers to the delocalization of the electrons with the participation of bonds of primary sigma character. Moreover, it is a permanent effect in which the localization of sigma electrons of C−H bond of an alkyl group is directly attached to an atom of the unsaturated system or to an atom with an unshared p orbital.
Now, from the above options, all the options are correct. Basically it is a delocalization of σ and π bonds and as a result it ends in the addition of bonds where there is no bond between C and H .Therefore, it is also called as no bond resonance. The hyper conjugation is as shown:
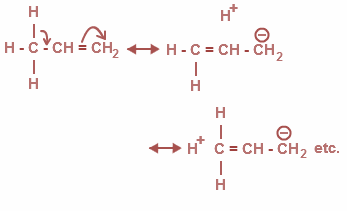
Moreover, the Baker-Nathan effect is used synonymously for hyper conjugation. It is a specific application for certain chemical reactions and types of structures.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: Hyper conjugation is used to rationalize a variety of chemical phenomena such as gauche effect, anomeric effect, beta-silicon effect, relative stability of carbocation, the rotational barrier of ethane and many more. Moreover, it has several properties such as bond length, dipole moments, heat of formation etc.
