Question
Question: Hydrolysis of an ester gives acid A and alcohol B. The acid reduces Fehling’s solution. Oxidation of...
Hydrolysis of an ester gives acid A and alcohol B. The acid reduces Fehling’s solution. Oxidation of alcohol B gives acid A. The ester is:
A) Methyl formate
B) Ethyl formate
C) Methyl acetate
D) Ethyl acetate
Solution
An ester is always formed by the reaction of an acid and an alcohol. It is a reversible reaction. Compounds which reduce Fehling’s solution usually have a −CO group in it. The formation of ester can be identified with the formation of a fruity smell.
Complete step by step answer:
The formation of an ester can be shown as;
R′OH+RCOOH→R′COOR+H2O
It is a reversible reaction also. By the hydrolysis of this ester, we can get back the acid and alcohol.
The simplest ester is methyl formate. It can be prepared by the following chemical reaction
CH3OH+HCOOH→HCOOCH3+H2O
The alcohol used here is methanol and the acid is formic acid.
Here it is given that the acid reduces Fehling’s solution. This is because of the presence of the −CO group. The structure of formic acid can be shown as:
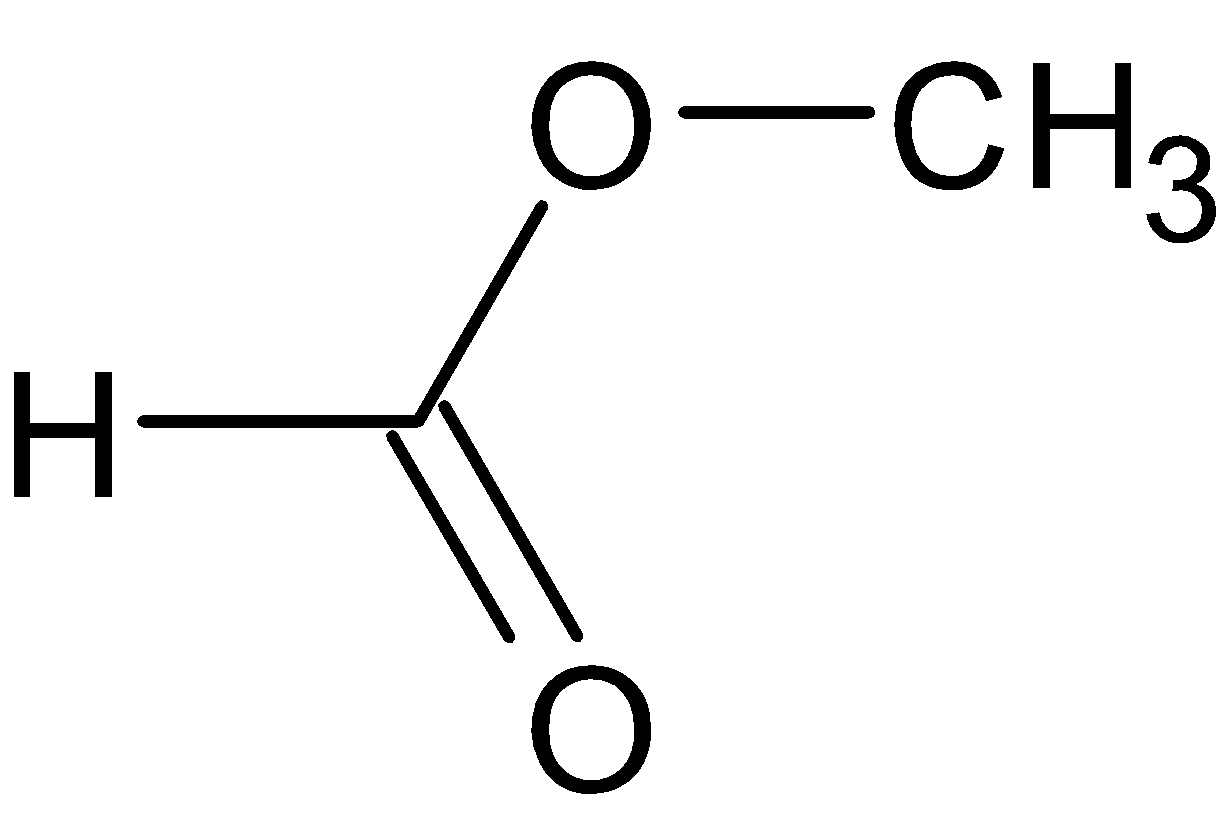
Because of the presence of that −CO group, we get a red precipitate after formic acid reacts with the Fehling’s solution.
The next condition given in the question is that this alcohol on oxidation gives the acid and this is shown by the equation;
CH3OH[O]HCOOH
From all this information, we came to know that the acid used here is formic acid and the alcohol is methanol and the ester is methyl formate
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional Information:
Fehling’s solution contains the mixture of two solutions namely Fehling’s solution A which is aqueous copper sulphate and Fehling’s solution B which is alkaline sodium potassium tartrate. It is commonly used to identify the
−COgroup in organic compounds.
Note: Esters are sweet smelling compounds. They are mainly used in the food industry as sweeteners and all. They are prepared by the reaction of suitable alcohol and acid at particular reaction conditions. The by-product formed in this reaction is water.
