Question
Question: Hydrazone of an aldehyde when heated with sodium ethoxide forms _____. This is known as _______ A....
Hydrazone of an aldehyde when heated with sodium ethoxide forms _____. This is known as _______
A.Hydroxyl group, wolf-Kishner
B.Alkane, wolf-Kishner
C.Alkane, Clemenson’s reduction
D.None of these
Solution
We can say that hydrazone are organic compounds, which are associated with ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen with the NNH2 functional group. We have to know that hydrazone could be formed by the action of hydrazine on aldehydes (or) ketones. In the formation of hydrazine from carbonyl compounds and hydrazine, a molecule of water is eliminated.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to remember that a hydrazone is the practical group with structure R1R2C=NNH2 . They resemble aldehydes or ketones, with a NNH2 bunch rather than the oxygen atom. They are prepared by reacting hydrazine with ketones or aldehydes:
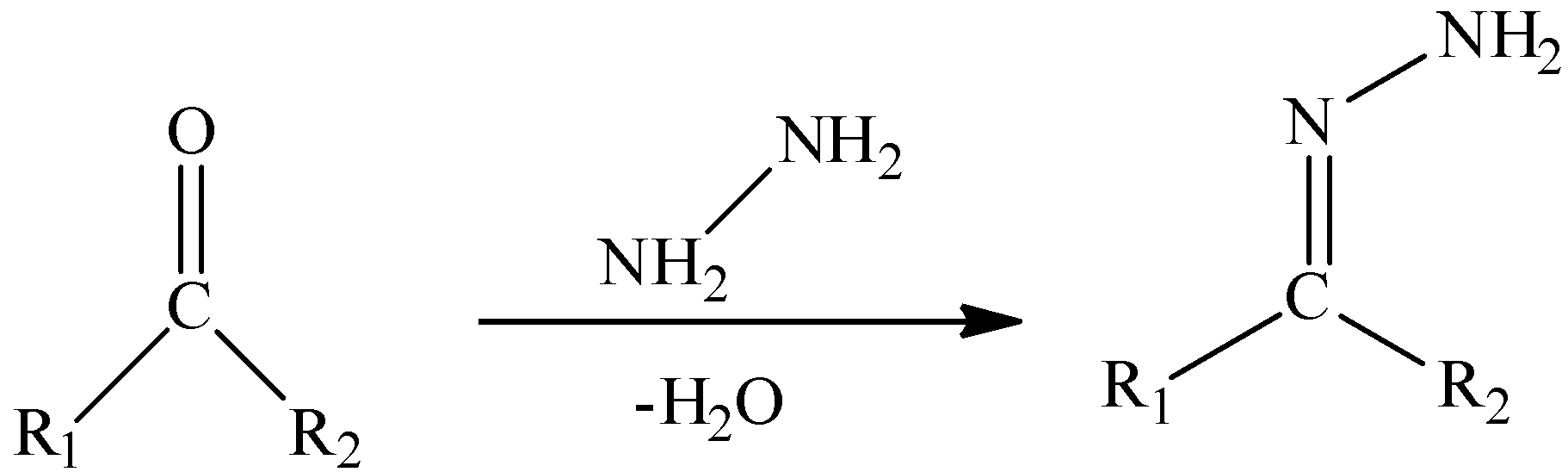
An aldehyde could be reduced down totally whenever made into a hydrazine and afterward treated with sodium ethoxide (Wolff–Kishner reduction).
We must need to remember that the Wolff–Kishner reduction is an organic reaction of lessening carbonyl groups; generally ketones and aldehydes to alkanes. It is completed in presence of dissolvable to accelerate reaction. It is completed in basic medium. In this way, it cannot be utilized for base delicate reagents. It is named after Nikolai Kishner and Ludwig Wolff.
Wolff Kishner reduction mechanism starts with the development of a hydrazone anion which at that point delivers the nitrogen molecule to produce a carbanion. This carbanion at that point reacts with the water in the framework to give a hydrocarbon. Regularly, diethylene glycol is utilized as a dissolvable for this technique.
The general reaction is,
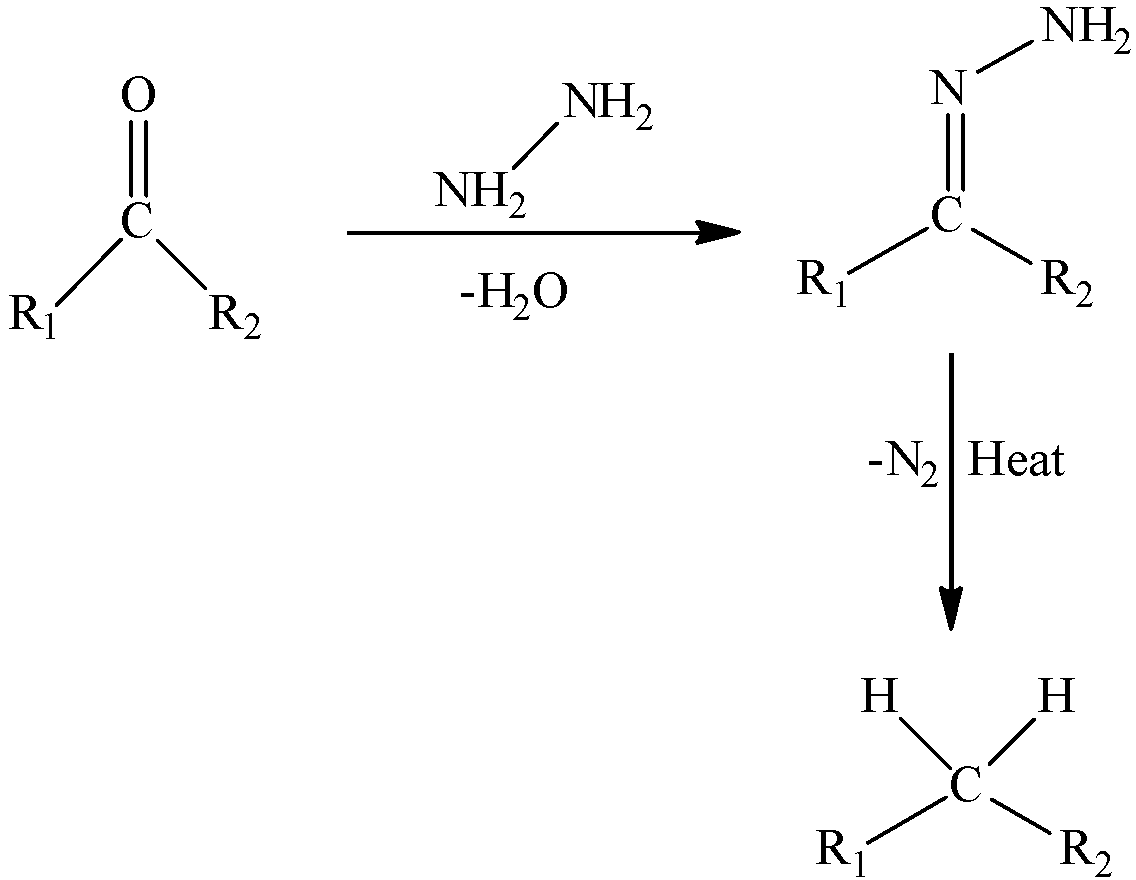
When heated with sodium ethoxide forms alkane with hydrazone of aldehyde. This is known as wolff-Kishner reduction. Option (B) is correct.
Note:
We have to remember that Wolff-Kishner Reduction converts carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. The second predominant side reaction is the reduction of aldehyde (or) ketone to the respective alcohol. After starting hydrolysis of the hydrazone, the derivative of free carbonyl is reduced by alkoxide to the carbinol. In general, formation of alcohol could be repressed by water exclusion (or) by addition of more hydrazine.
