Question
Question: Hybridization of sulfur in \({{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\) is: (a)- \(sp\) (b)- \(s{{p}^{2}}\) (c)- ...
Hybridization of sulfur in H2SO4 is:
(a)- sp
(b)- sp2
(c)- sp3
(d)- sp3d2
Solution
The hybridization can be calculated with the number of valence electrons of the central atom, number of monovalent atoms/ groups surrounding the central atom, charge on the cation, and charge on the anion.
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization is defined as the mixing of the atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom but having slightly different energies so that redistribution of energy takes place between them which results in the formation of new orbitals with similar energies and similar shapes. The orbitals thus formed are known as hybrid orbitals.
In H2SO4 the central atom is sulfur and it is surrounded by four oxygen atoms and two hydrogen atoms.
For calculating the number of hybrid orbital or hybridization of the central atom we can use the formula:
X=21no. of valence electrons of central atom !!!! + !!!! no. of monovalent atoms !!!! !!!! charge on cation !!!! + !!!! charge on the anion !!!! -
X=21[VE+MA−c+a]
So, in H2SO4the central atom sulfur has 6 valence electrons.
There are two monovalent atoms present in H2SO4. Oxygen is a divalent atom.
There is no cationic charge in H2SO4.
There is no anionic charge in H2SO4
So, by putting all these in the equation, we get
X=21[6+2−0+0]=28=4
The value of X is 4, therefore, the hybridization issp3.
The structure of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is given below:
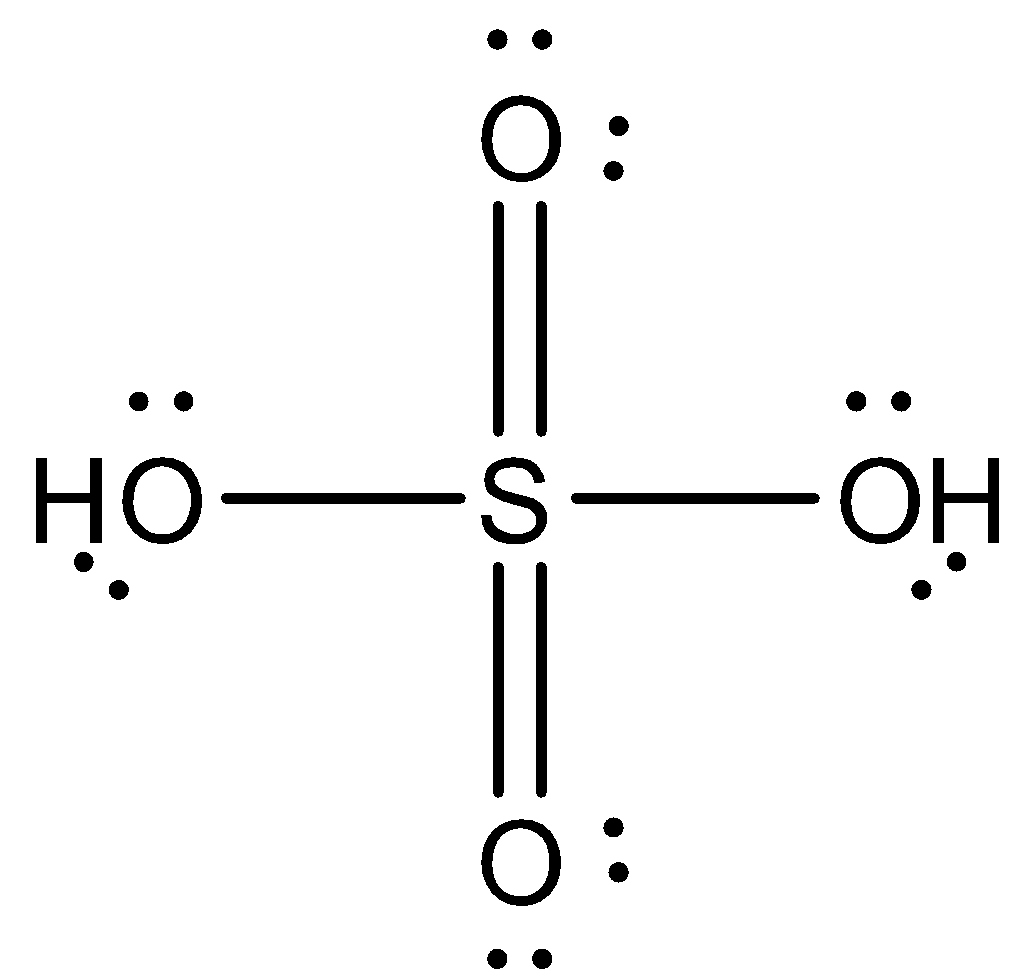
Because of sp3hybridization, the structure of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is tetrahedral.
Therefore the correct answer is an option (c)- sp3
Note: Only monovalent atoms can be considered. For divalent ion, MA = 0. By calculating the hybridization the structure can be predicted, but due lone pair the structure will get changed. So for predicting the shape, lone pairs should be considered.
