Question
Question: Human body temperature is maintained by- (a)Hypothalamus (b)Medulla oblongata (c)Pituitary gla...
Human body temperature is maintained by-
(a)Hypothalamus
(b)Medulla oblongata
(c)Pituitary gland
(d)Cerebral cortex
Solution
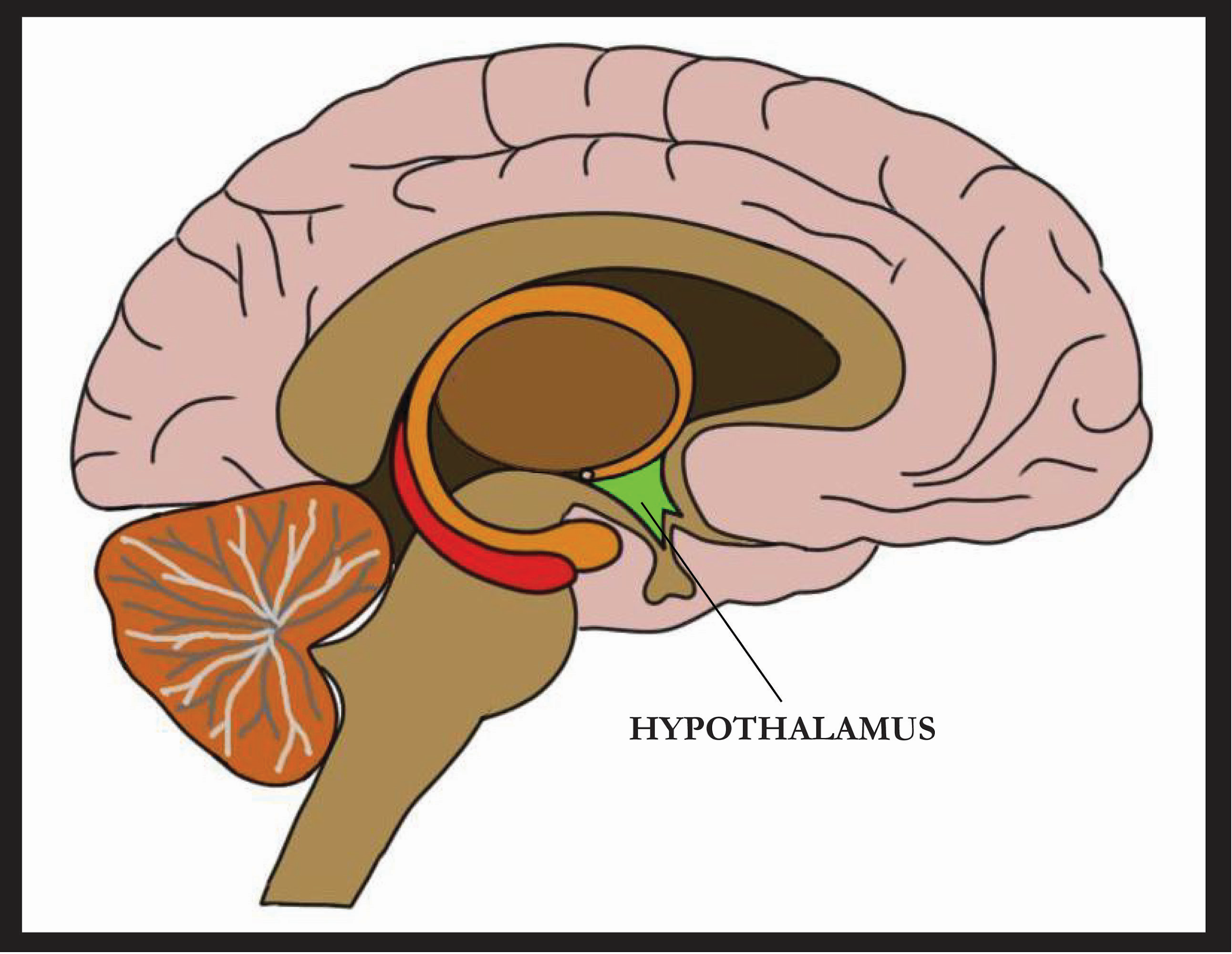
It is a small brain area. It's situated near the pituitary gland, at the base of the brain. Although it is very small, many important roles, including the release of hormones, play a crucial role. Body Temperature Control.
Complete answer:
A part of the forebrain is the hypothalamus. It is the brain's thermoregulatory center. By means of a complex thermostat system, the body temperature is maintained at approximately 30 degrees C.
A part of the brain that includes a number of small nuclei with a range of functions is the hypothalamus. One of the hypothalamus's most important functions is to connect the nervous system through the pituitary gland to the endocrine system. Below the thalamus, the hypothalamus is located and is part of the limbic system. It forms the ventral portion of the diencephalon in neuroanatomy terminology. A hypothalamus is present in all vertebrate brains. It is the size of an almond in humans.
Additional Information: The medulla oblongata is a long, stem-like structure that forms part of the brainstem. It is anterior to the cerebellum and partly inferior to it. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing that is autonomic (involuntary).
The pituitary gland is a small pea-sized gland that plays a major role in the control and overall well-being of essential body functions. It is referred to as the 'master gland' of the body because it regulates the function of most other glands that secrete hormones.
The outer layer of neural tissue of the brain cerebrum in humans and other mammals is the cerebral cortex (plural cortices), also referred to as the cerebral mantle. Most of the cerebral cortex consists of a six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of an allocortex.
So, the correct answer is ‘Hypothalamus’.
Note: The dorsomedial and ventromedial nuclei are involved in the regulation of the feeding impulse in the tubular portion of the hypothalamus. The former controls the desire to feed, while the latter controls the sense of fullness. In regulating feeding, the lateral nucleus is also essential.