Question
Question: 
Number of possible stereoisomers in C
(1)2
(2)3
(3)4
(4)5
Solution
We know that isomers that possess different spatial atomic arrangement but same atomic connectivity are termed as stereoisomers. There are two types of stereoisomers, geometric isomers and optical isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, first we have to complete the reaction and then we have to find out the stereoisomers of C.
First the butan-2-ol reacts with PCC. We know that PCC is an oxidizing agent. It converts alcohol to carbonyl groups. So, the product A formed is,
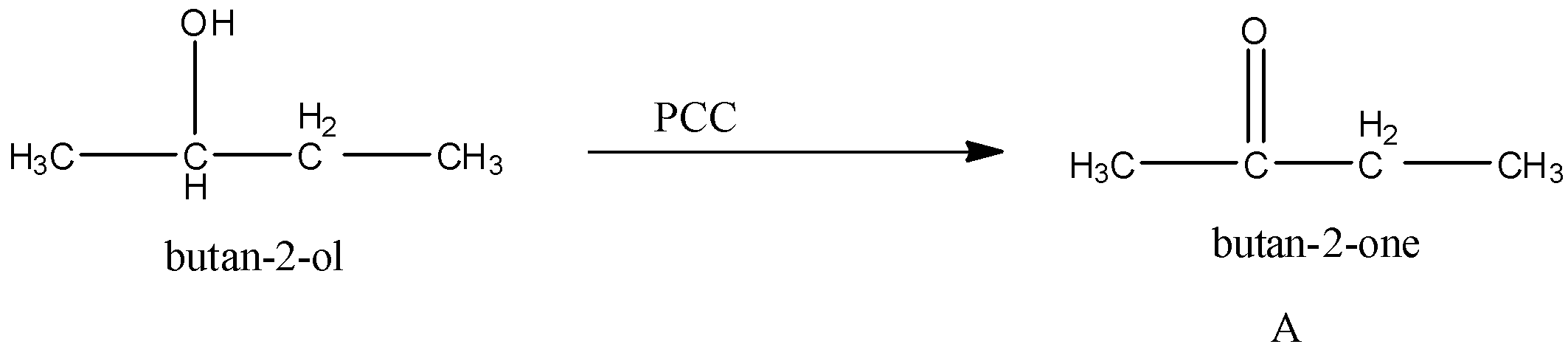
Now, A (butan-2-one) reacts with SeO2. Selenium dioxide converts an active methylene group to a carbonyl group. Methylene group is the carbon atom that is bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
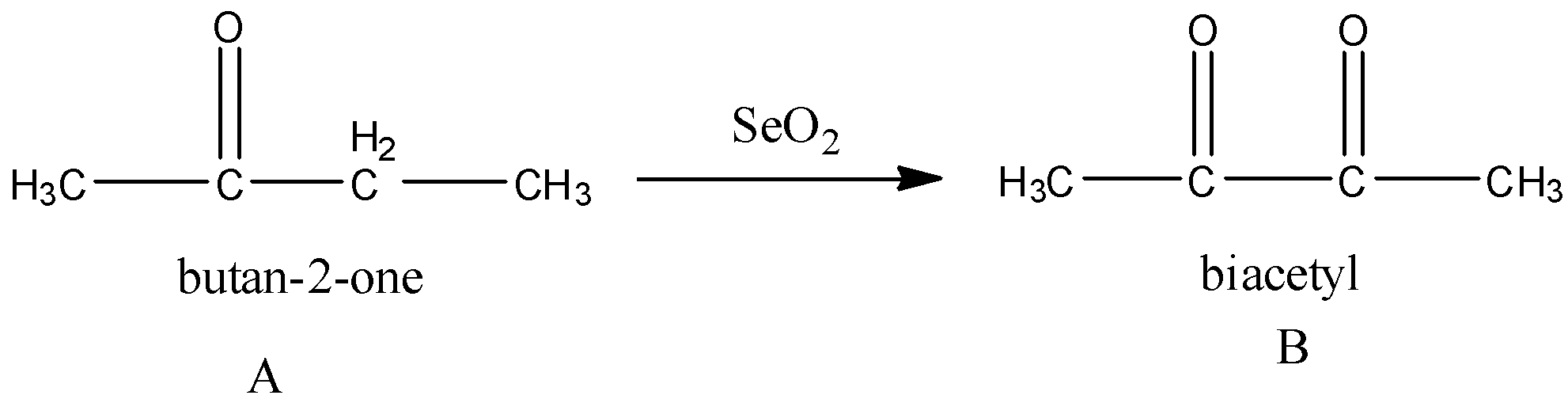
Next, B reacts with LiAlH4. We know that lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) is a reducing agent. It can reduce ketone, carboxylic acid, aldehyde to alcohol groups.
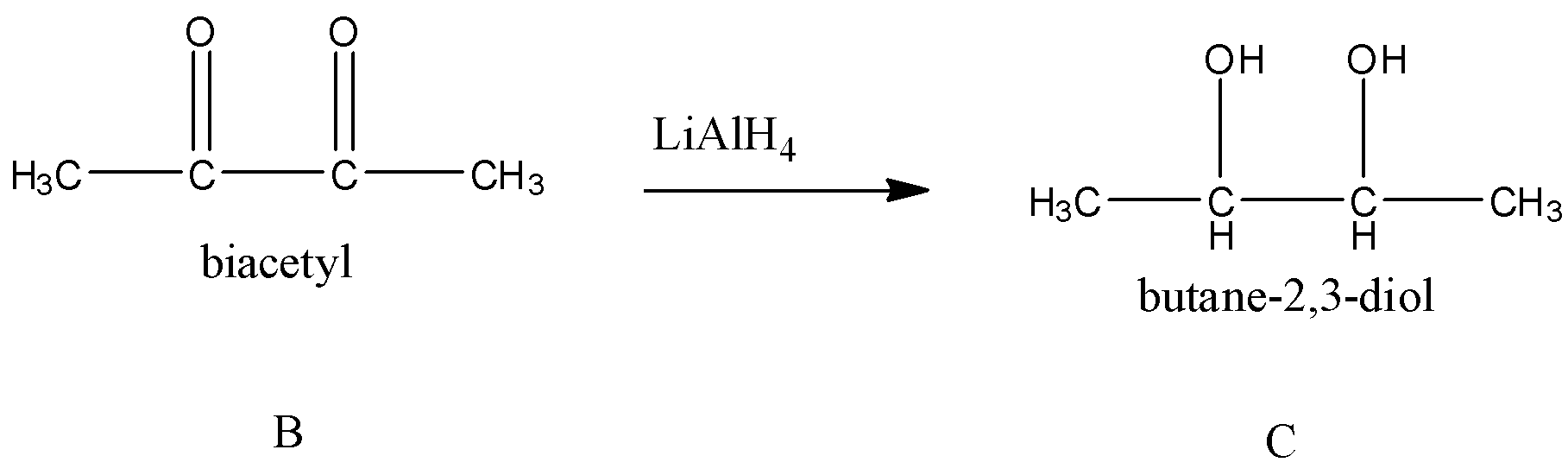
So, the compound C formed is butane-2,3-diol. Now, we have to find out the number of isomers for butane-2,3-diol.
We know the formula to calculate the number of stereoisomers is 2n. Here, n represents the number of chiral centres.
In butane-2,3 diol, two chiral centres are present.
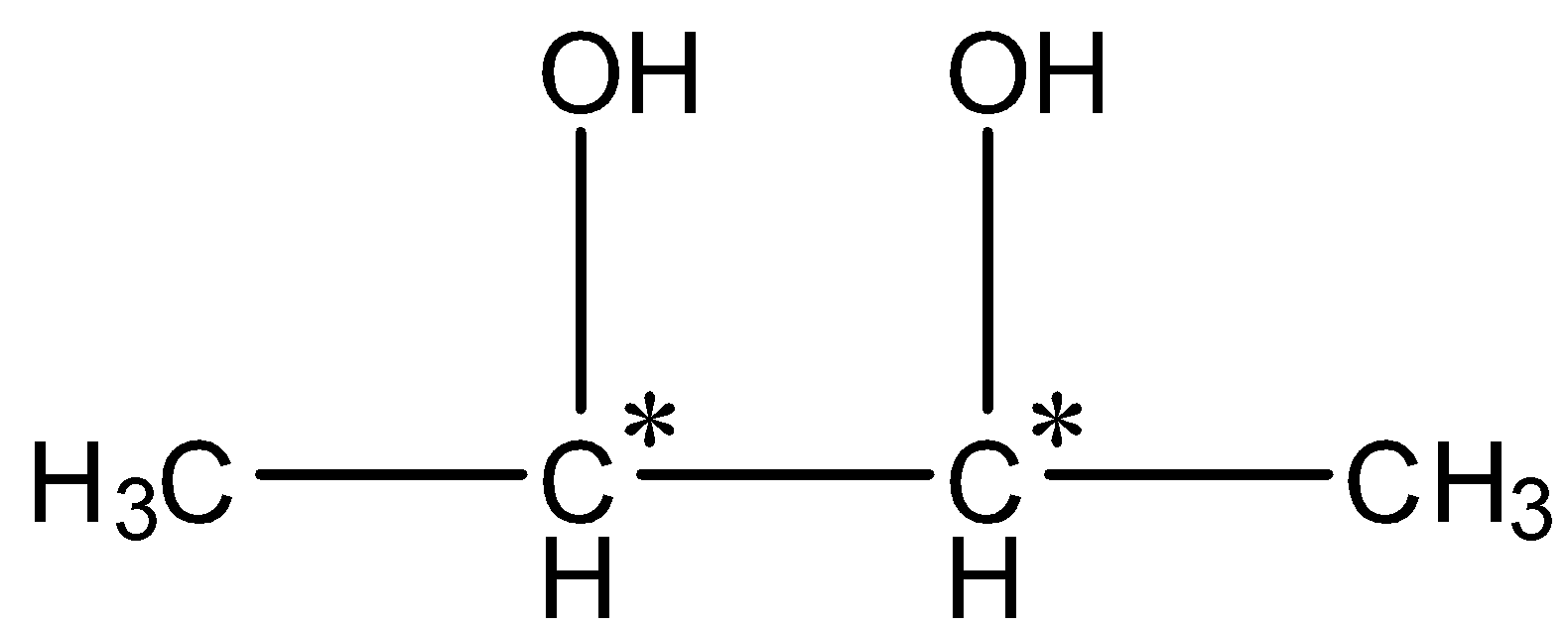
So, the number of stereoisomers=22=4. Therefore, the number of stereoisomers is 4.
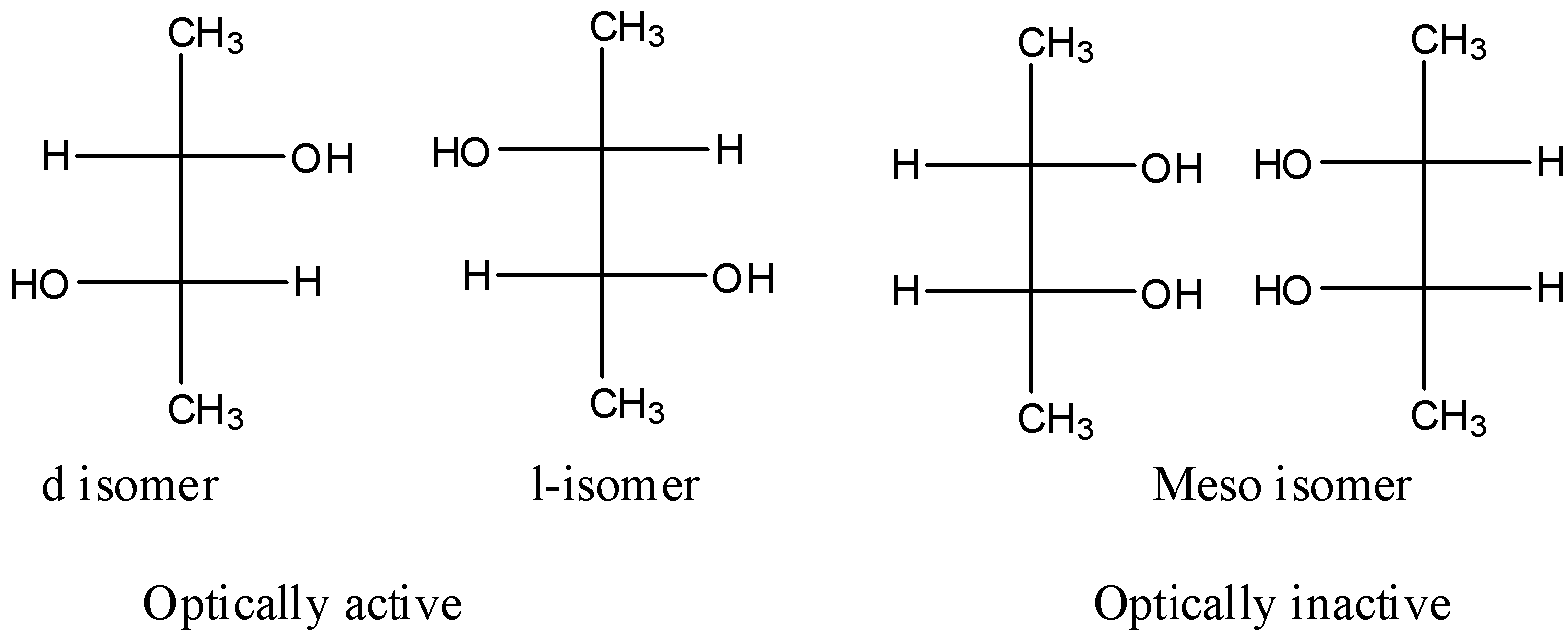
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Note:
Always remember that a compound can have stereoisomers only if it possesses chiral centres. Chiral central is the atom in which all the four groups attached are different. To identify whether an atom is chiral or not, we have to look at the groups bonded to it. If all the bonded groups are different it indicates that the atom is a chiral centre.
