Question
Question: How would you explain the structural difference between an aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid and ...
How would you explain the structural difference between an aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid and an ester?
Solution
The question is based on the knowledge of carbonyl compounds that is the compounds containing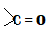 as a functional group. This includes aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives such as esters.
as a functional group. This includes aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives such as esters.
Complete step-by-step answer: The question asks about the structural difference between an aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid and an ester. Let us see the difference in a short tabular form.
| Aldehyde | Ketone | Carboxylic acids | Esters |
|---|---|---|---|
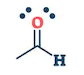
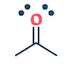
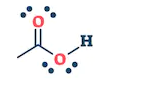
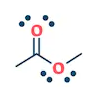
| They are the class of organic compounds in which a carbon atom shares a double bond with an oxygen atom and a single bond with hydrogen atom, and a single bond with another atoms or groups of atoms. | Ketone are the class of organic compounds having the presence of carbonyl group in which carbon atom is covalently bonded to an oxygen atom and remaining two bonds other carbon atoms or hydrocarbon radicals | They are the class of organic compounds in which a carbon atom is bonded to an oxygen atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group (OH) by a single bond. A fourth bond links the C atom to H or to any univalent combining group. | They are the class of organic compounds in which -OH group of carboxylic acid is replaced by -OR group. Where R= any alkyl group. They are also termed as acid derivatives. |
 |  |  |  |
Note: Carboxylic acids derivatives such as esters get converted into their corresponding carboxylic acids by hydrolysis which takes place either in acidic or basic medium. There are many tests in which different compounds give different results based on their structure.
