Question
Question: How would you explain the nitrogen cycle?...
How would you explain the nitrogen cycle?
Solution
The nitrogen cycle is a multifaceted bio, geo, and chemical cycle during which the element nitrogen is renewed and regenerated from its inactive distinctive molecular form (N2) into an arrangement that is useful in organic processes. Nitrogen is considered as the building block of a living cell.
Complete answer:
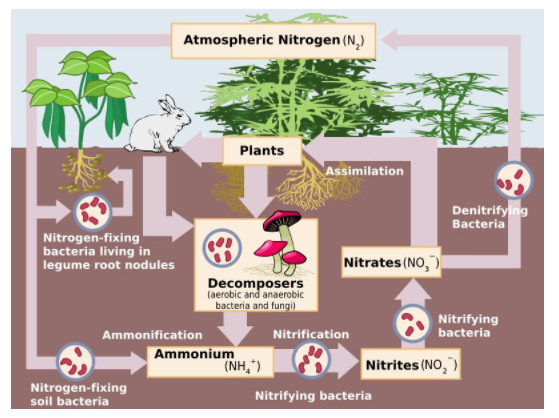
The steps in the nitrogen cycle are observed of:
Nitrogen Fixation: It is described as a technique by which the molecular nitrogen in the atmosphere is transformed into the compound ammonia or associated nitrogenous complexes in soil. The atmospheric nitrogen is in the structure of molecular dinitrogen, a rather non-reactive molecule that is metabolic which is vain to all but helpful to a few microorganisms.
Ammonification: The procedure of Ammonification typically refers to any chemical response whereby the agencies of NH2 are modified into the compound ammonia or its ionic form, which is ammonium (NH4+), as a give up product. Thus, we can see that it is a manner in which natural nitrogen existing in plants and animals after their death is changed to ammonium ions.
Nitrification: It is a procedure in which ammonium ions are modified into nitrates. The thing nitrogen up taking by using plants: The nitrate which is fashioned in the technique of Nitrification is used through most florae as inorganic metabolites and can be modified by means of them into amino collections and other nitrogen-comprising mixtures.
The fixation of Nitrogen: The system of reduction of different nitrogen to the ammonium ion by microorganisms such as Rhizobium present in the leguminous plants.
The Denitrification: The method of discount of closing nitrates to nitrogen fuel or nitrous oxide by using certain microorganisms.
Note: It is massive to observe that quite a number kinds of microorganisms play a vital function in each of the following steps. Nitrous oxide N2O which has extended impact in the atmosphere as an impact of agronomic fertilization, sweltering of biomass, livestock, and feedlots, and manufacturing sources.
