Question
Question: How would you differentiate between monosubstituted and disubstituted alkenes?...
How would you differentiate between monosubstituted and disubstituted alkenes?
Explanation
Solution
We know that alkene is a hydrocarbon containing one or more Carbon-Carbon double bonds. Some examples of alkene are ethene, butane, etc. Alkenes with 2 to 4 carbon atoms are gases at room temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s learn the differences between monosubstituted and disubstituted alkene.
| Monosubstituted alkene | Disubstituted alkene |
|---|
- A monosubstituted alkene is the alkene in which double bonded carbon atoms are bonded to only one carbon atom| 1) It is the alkene in which double bonded carbon atoms are bonded to two other carbon atoms.
- As only one substitution present, therefore, it is known as monosubstituted alkene.| 2) As there are two substitutions, therefore, it is known as disubstituted alkene.
3)For example,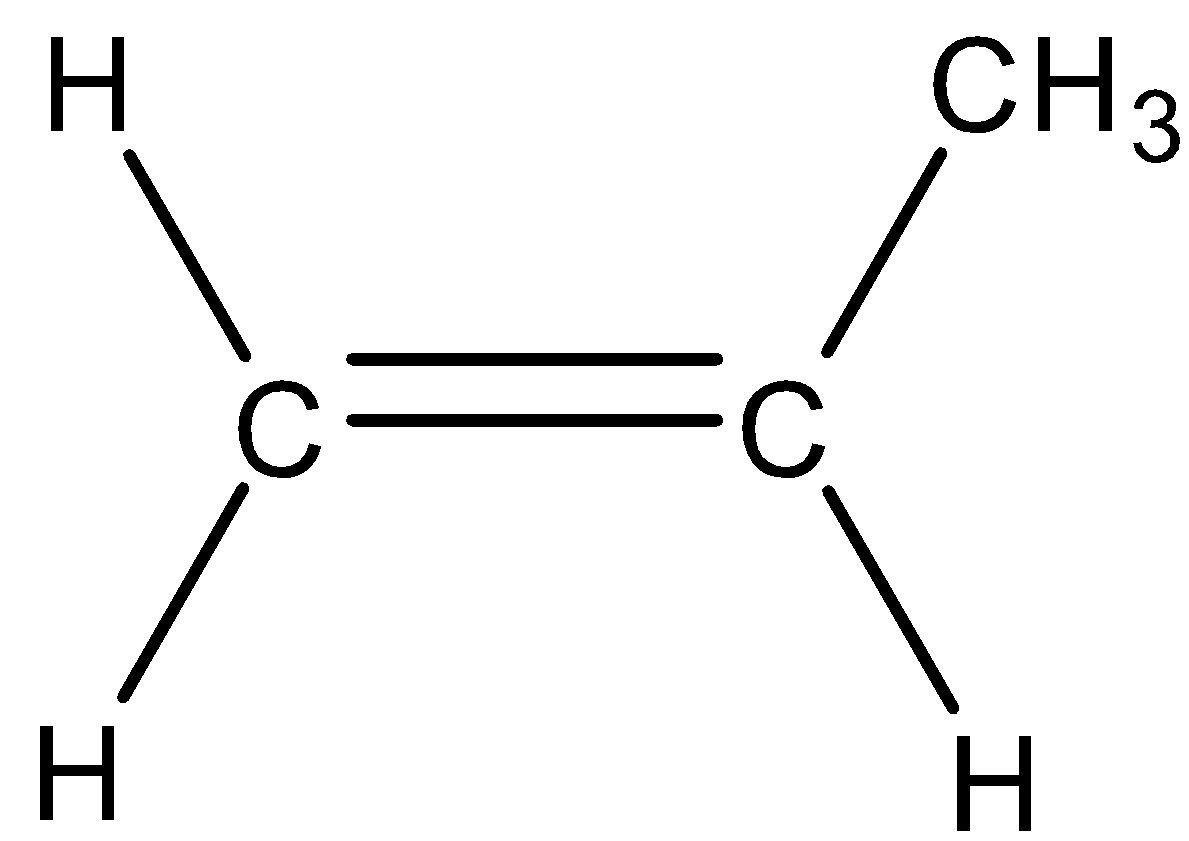 | 3)For example,
| 3)For example,
- Stability is less | 4)Stability is high
Additional information:
Let’s understand some important points of alkene.
- Most physical and chemical properties of alkenes are similar to those of alkanes.
- With the increase of molecular mass, the boiling points of the alkenes increases.
- The increase of branching of alkenes results in greater volatility and lower boiling points.
- Alkenes can undergo polymerization.
- Alkenes composed of both sigma and pi bonds.
Let’s discuss some chemical properties of alkenes. - Alkenes react with bromine to form vicinal dihalide. Among the halogens, bromine does not undergo reaction with alkenes.
C2H4+Br2→C2H4Br2 - Alkenes undergo reduction reaction with hydrogen in presence of platinum or nickel to form alkanes.
C2H4+H2→CH3CH3
Note: It is to be noted that the tetrasubstituted alkene is the alkene in which double bonded carbon atoms are bonded to three other carbon atoms. For example,
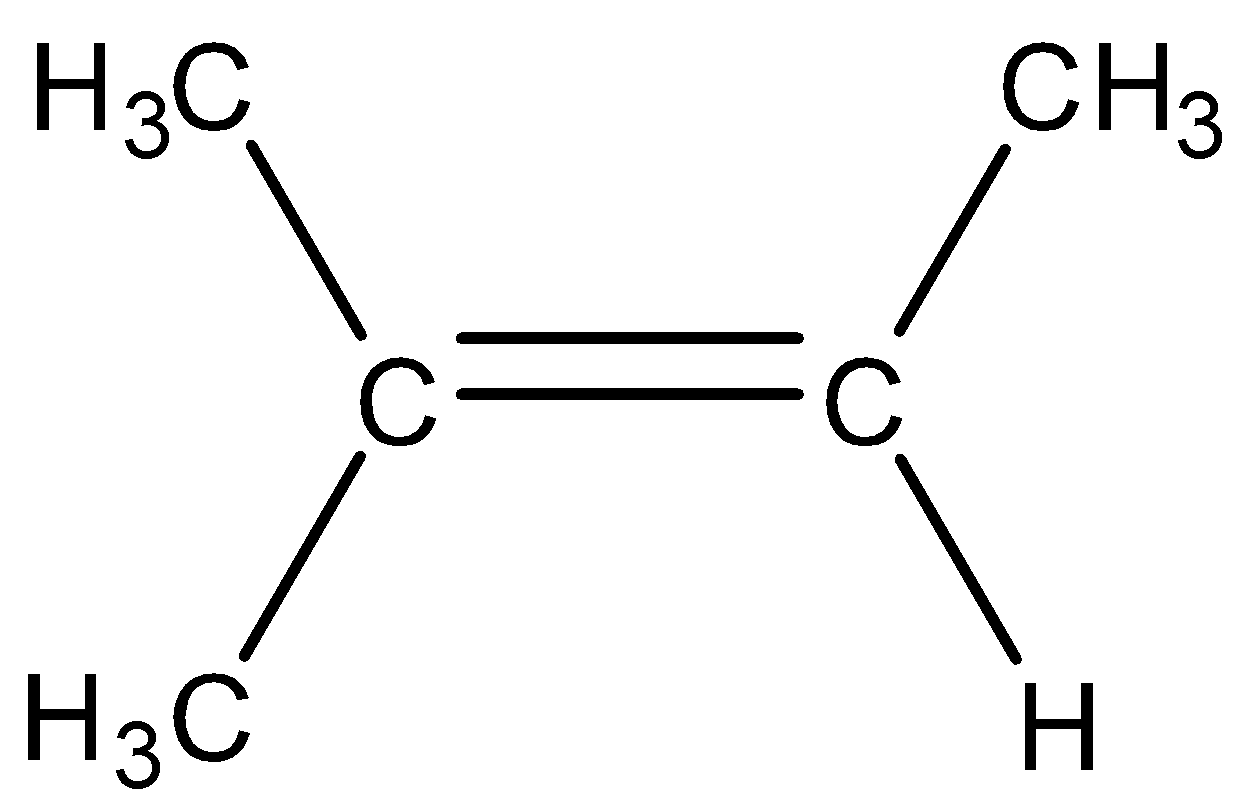
As there are three substitutions, therefore, it is known as tetrasubstituted alkene.
