Question
Question: How will you obtain p-chlorobenzaldehyde from benzene?...
How will you obtain p-chlorobenzaldehyde from benzene?
Solution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction: It is an organic reaction in which an electrophilic group (generally hydrogen atom) gets replaced with an electrophile when reacted in the presence of required reagent. Some examples of electrophilic substitution reactions are halogenation, nitration, Friedel craft alkylation etc.
Complete answer:
For the given conversion, the following steps are involved in the reaction mechanism:
Step-1: The benzene molecule undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction i.e., halogenation reaction in the presence of Br2 and FeBr3 . The reaction proceeds as follows:
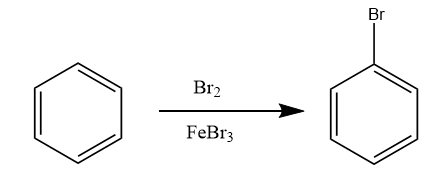
Step-2: The bromobenzene further reacts with magnesium metal in the presence of ether to form Grignard reagent of type R−Mg−X . The reaction proceeds as follows:
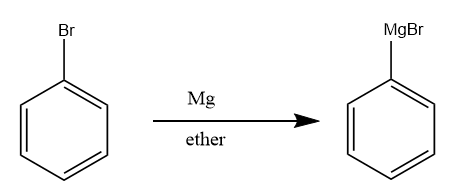
Step-3: The Grignard reagent formed, reacts with formaldehyde in the acidic medium to form the benzyl alcohol. The reaction takes place as follows:
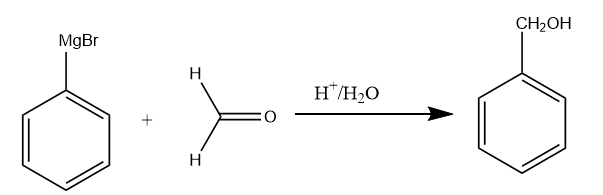
Step-4: The benzyl alcohol again undergoes a halogenation reaction in the presence of Cl2 and FeCl3 . As there is an alkyl group present on the benzene which is ortho-para directing, so the formation of para chlorobenzyl alcohol will take place. The reaction proceeds as follows:
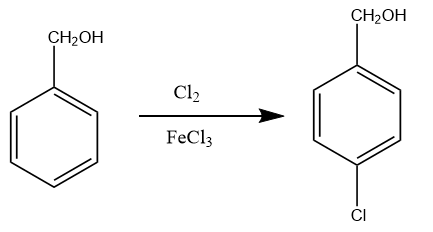
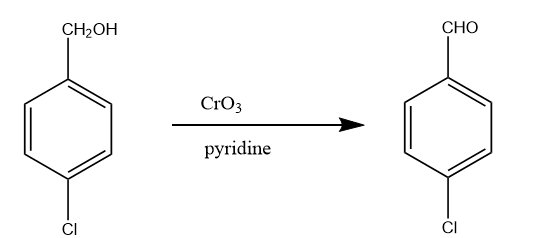
Step-5: Now the alcoholic group of benzyl alcohol is oxidized when para chlorobenzyl alcohol reacts with chromium trioxide in the presence of base like pyridine. Then, the final product is obtained i.e., para chlorobenzaldehyde. The reaction takes place as follows:
Note:
It is important to note that in this conversion, we cannot first substitute the chlorine group to the benzene ring because it is a good leaving group and it will eventually be replaced and the benzene ring will tend to show nucleophilic substitution reaction under specific conditions.
