Question
Question: How will you make (obtain) from chloroform: A. Chloretone B. Phenyl isocyanide C. Acetylene ...
How will you make (obtain) from chloroform:
A. Chloretone
B. Phenyl isocyanide
C. Acetylene
D. Salicylaldehyde
Solution
Chloroform is an organic compound with chemical formula CHCl3. It is composed of carbon, hydrogen and three chlorine atoms. It is used as a chlorinated solvent in organic synthesis.
Complete step by step answer:
The chloroform is a chlorinated organic compound. It is polar solvent and readily dissolves most of the organic compounds. It is also called trichloromethane or chlorinated solvent. It is colourless, volatile and dense liquid and has a characteristic strong smell.
Let us synthesize the given compounds using chloroform as a starting material.
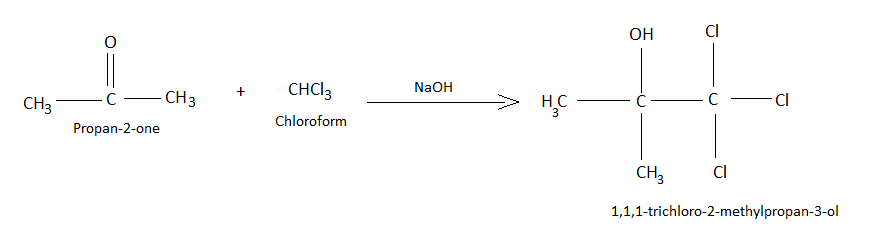
A. Chloretone.
Chloretone is a chemical used as a preservative. The compound is also known as chlorobutanol, or chlorbutol. The IUPAC name is 1,1,1 -trichloro-2-methyl-2-propanol. It is prepared by reaction acetone with chloroform in presence of sodium hydroxide.
B. Phenyl isocyanide
Phenyl isocyanide is an organic compound containing an isocyanate functional group. Phenyl isocyanide is prepared by treating phenyl amine or aniline with chloroform in presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide. The reaction is named as carbylamine reaction. This reaction is used as a confirmatory test for the identification of aromatic amine. The generation of unpleasant smell indicates that an isocyanide has formed in the reaction.
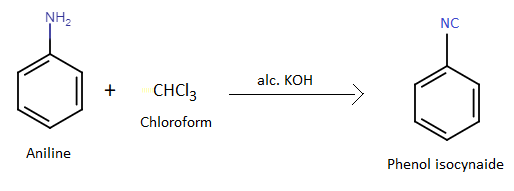
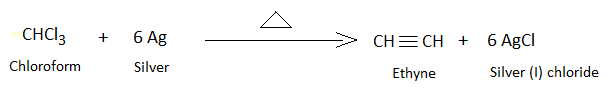
C. Acetylene
Acetylene is the primary ethyne hydrocarbon with chemical formula C2H2. It is formed by the reaction of chloroform and silver power under heating conditions. AgClis formed as the side product.
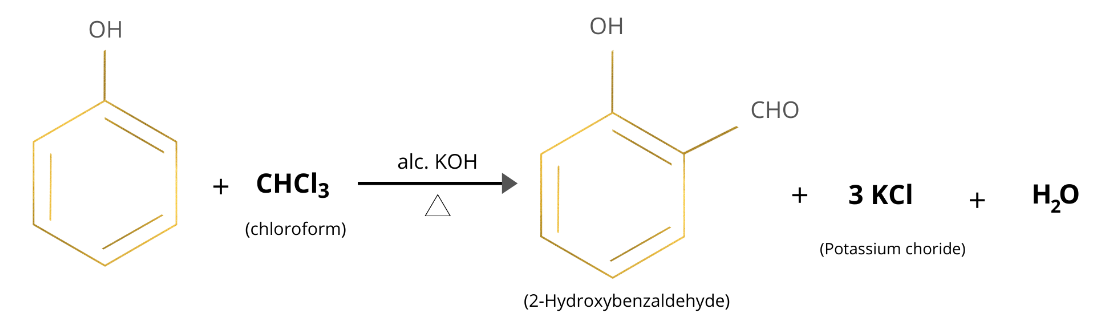
D. Salicylaldehyde
Salicylaldehyde is ortho-hydroxy benzaldehyde or 2-hydroxy benzaldehyde. Salicylaldehyde is prepared using Reimer Tiemann reaction. It is synthesized by reaction phenol with chloroform in presence of alcohol KOH. An aldehyde group is introduced on the benzene ring ortho to the hydroxyl group.
Note:
The mechanism of these reactions include the formation of dichlorocarbene from chloroform by loss of hydrogen and a chlorine atom using basic conditions. The dichlorocarbene acts as an electrophile and attacks electron-rich species like alkene or benzene rings. It also acts as a nucleophile and attacks electron deficient carbonyl carbon.
