Question
Question: How will the P.E.C change on decreasing the wavelength of incident radiation for a given metal?...
How will the P.E.C change on decreasing the wavelength of incident radiation for a given metal?
Solution
Einstein’s photoelectric equation states that the energy of a photon hitting the surface of a metal is the sum of the work function of the metal and the energy of the released electron from the metal.
Formula used:
Einstein’s equation for photoelectric effect is given by,
Ep=W+Ee
where, Ep is the energy of the photon, W is the work function of the metal and Ee is the kinetic energy of the electron.
Energy of a photon is given by,
E=hν
where, h is Planck's constant and ν is the frequency of the photon.
Relation between wavelength and frequency is given by,
λ=νc
where,c is the velocity of light and ν is the wavelength.
Complete step by step answer:
We know from photoelectric effect, when a photon hits the surface of any metal a photoelectron comes out. The minimum energy required to release the electron is known as the work function of that metal.
Einstein’s equation for photoelectric effect states that, energy of a photon hitting any metal surface is the sum of the work function of the metal and the energy of the released electron. It is given by, Ep=W+Ee. Now, this kinetic energy is converted to electrical energy if joined between two terminals of a circuit.
So, we can rewrite the equation in terms of current as, λhc=W+eIR where R is the resistance between the terminals. So, we can see that if the resistance and all other things are constants in the equation the current and the wavelength will form a hyperbolic curve of the form, (x+k)y=c.
Hence the current will change with the wavelength in a hyperbolic curve, starting from zero current and a maximum wavelength due to the stopping potential. Since, for I=0 the equation is hc=λWmeaning wavelength will have a maximum value of λ=Whc. The wavelength will decrease as the current increases. So, the curve can be shown as,
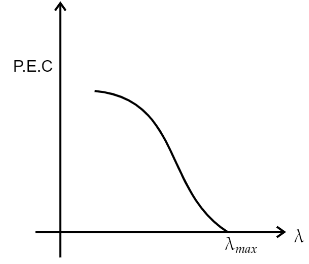
Note: The curve of the wavelength versus the current is opposite to the curve of frequency versus current, since frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength. When drawing the curve you can use this knowledge of frequency current curve to draw the wavelength versus current graph easily.
