Question
Question: How to remember molecular bond angles?...
How to remember molecular bond angles?
Solution
Atoms of a molecule, when arranged in a three-dimensional structure, give the molecular geometry of that molecule. There are various geometrical parameters that determine the shape of a molecule and the position of the atoms in it. Some of the parameters are molecular bond length, torsional angles, molecular bond angles, etc.
Complete answer:
We know that when there is a shared pair of electrons between two atoms, a covalent bond is formed. These covalent bonds are either single bonds, double bonds or triple bonds. The properties of these bonds, like its length and angles are used to determine the geometry of a molecule.
Now, a molecular bond angle can be defined as the geometric angle which is formed across two bonds of a molecule between three atoms.
There are various factors that determine the molecular geometry, and by extension the molecular bond angle, for example the number of bond pairs in the molecule, the number of lone pairs, presence of any unpaired electron, and the location of the nuclei and its electrons.
These along with the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory can help us determine the molecular geometry and molecular bond angles. The most common shapes among simple molecules are as follows-
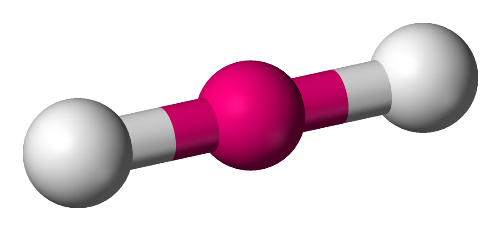
1. Linear: In this model, the atoms are set at an angle of 180∘ and form a linear shape.
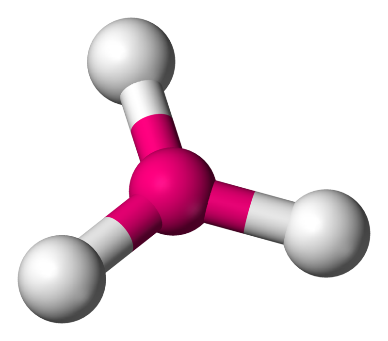
2. Trigonal Planar: In this model, the atoms are set at an angle of 120∘ and form a shape which has one flat plane and is triangular.
3. Angular: In this model, the atoms are set at an angle of 105∘ and have a bent or a V-shape.
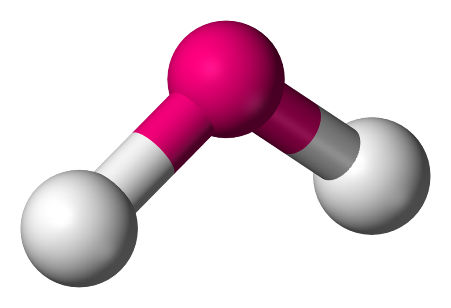
4. Tetrahedral: In this model, the atoms are set at an angle of 109.47∘ and has four faces since four atoms are bonded on the central atom
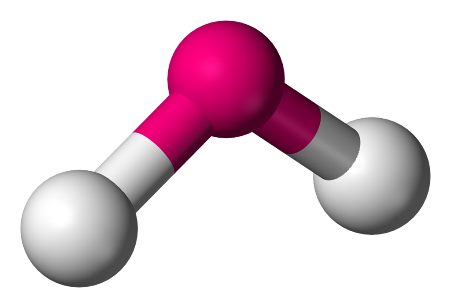
5. Octahedral: In this model, the atoms are set at an angle of 90∘ and has eight faces.
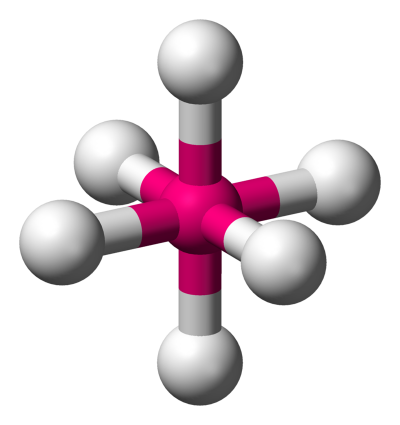
Hence, these shapes and their corresponding angles can be used to approximately determine and remember the molecular bond angles.
Note:
It must be noted that the above molecular bond angle values are shown by molecules in ideal conditions. When factors like electron-electron repulsion, or dipole moments are taken into account, the value of these molecular bond angles changes. The exact angle, hence can only be calculated using computers and are different for different types of molecules.
