Question
Question: How to determine the stability of gauche and anti conformation?...
How to determine the stability of gauche and anti conformation?
Solution
Conformational isomers are interconverted by rotations around a single bond. They are classified into two different types that are staggered and eclipsed conformation. In eclipsed conformation, hydrogens are connected to two carbons closest to each other. In staggered, hydrogens are connected to two carbons as far as possible.
Complete answer:
If a compound has higher energy than that compound will be less stable.
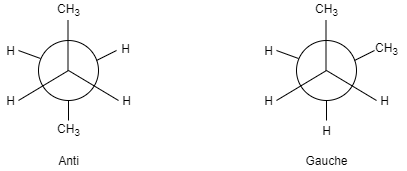
Let us take an example of staggered conformers of butane in which we compare the anti and gauche conformers.
In gauche isomers, there is no interaction between the hydrogen- hydrogen and methyl –hydrogen, hence its energy will be zero but we can see a butane gauche interaction that increases the energy by 0.9KCalmol−1. Therefore, for gauche conformers the energy of the molecule will be 0.9KCalmol−1.
Let us see the structure of gauche conformers-
In anti conformers, there is no interaction between the hydrogen- hydrogen, methyl-hydrogen, methyl-methyl. Hence the molecule energy will be zero.
Let us see the structure of anti conformers-
As we can see here the energy of gauche is much higher than the anti therefore we can say that the stability of anti will be more than gauche.
The stability of the molecule is inversely proportional to the energy of the molecule.
Note: In staggered conformations, the group of atoms are arranged in 60∘ dihedral angle whereas in eclipsed conformations, the group of atoms are arranged in 0∘ dihedral angle.
Staggered conformations show high steadiness whereas eclipsed conformation shows low steadiness.
