Question
Question: How many structural isomers can be formed by monochlorination of methylcyclohexane?...
How many structural isomers can be formed by monochlorination of methylcyclohexane?
Solution
Methylcyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the methyl group on cyclohexane. The chlorination can be done by any chlorinate ng agent like chlorine gas. The monochlorination of methylcyclohexane forms five structural isomers. The chlorine will add at ortho, meta, para, hypso and inside chain means in the place of hydrogen in the methyl group.
Complete answer:
The compounds with the same molecular formula but different structure can exhibit structural isomerism. The compounds were known as structural isomers.
Methylcyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula of C7H14 . It is simply written by writing the methyl group on cycloalkane.
The structure of methylcyclohexane is
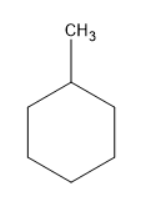
Monochlorination means the addition of chlorine atom. When chlorine atom is added to the above structure.
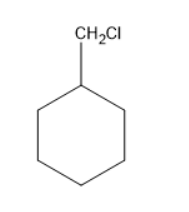
Chlorine will substitute at one of the hydrogens in methyl group forms a compound as follows:
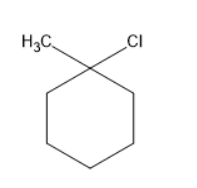
Chlorine will substitute at the hypso position forms a compound as follows:
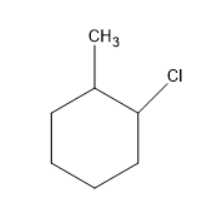
Chlorine will substitute at the ortho position forms a compound as follows:
Chlorine will substitute at the meta position forms a compound as follows:
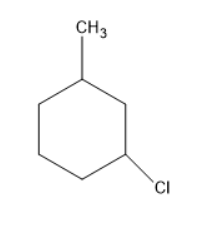
Chlorine will substitute at the para position forms a compound as follows:
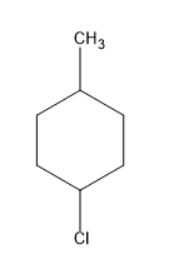
Thus, five structural isomers were formed by monochlorination of methylcyclohexane.
Note:
Generally, the ortho, meta and para isomers were the position isomers. Position isomers are also coming under the structural isomers. All the above five structures have the same chemical formula but difference in structures only. Chlorination is an electrophilic substitution reaction in which the hydrogen is replaced by the chlorine.
