Question
Question: How many sperms are produced from 200 secondary spermatocytes?...
How many sperms are produced from 200 secondary spermatocytes?
Solution
In the process of an anisogamous sexual reproduction, sperm is the male reproductive cell or gamete. Animals generate motile sperm with a flagellum tail, known as spermatozoa. However, some red algae and fungus create non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants have non-motile sperm inside their pollen, but ferns and other gymnosperms have flagellated sperm.
Complete answer:
The reproductive system of a male is specially adapted to generate, store, and transfer sperm. Male reproductive organs, unlike female genitalia, are located on both the interior and exterior of the pelvic cavity. They are the testes (testicles), the duct system (epididymis and vas deferens (sperm duct), the accessory glands (seminal vesicles and prostate gland), and the penis. Sperm production usually takes place in the testicles.
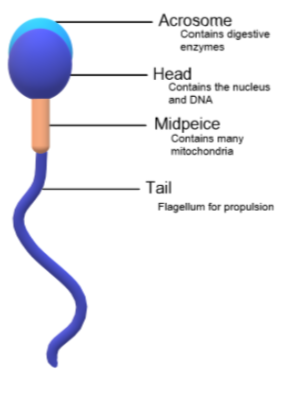
Image showing sperm anatomy
When the undifferentiated primordial germ cells reach sexual maturity, they divide numerous times via mitosis to form a huge number of spermatogonia. Each spermatogonium actively develops to become a bigger primary spermatocyte, which then divides into two subsequent divisions known as maturation divisions. The first division of maturation is the reduction or meiotic.
The primary spermatocyte which is known as Elence, splits into two haploid daughter cells known as secondary spermatocytes. Both secondary spermatocytes are now going through a second maturation division, which is a normal mitotic division, to produce four haploid spermatids.
As a result, each secondary spermatocyte produces two spermatids, which undergoes conversion to generate two sperm. Since both secondary spermatocytes produce four sperms in total. Hence, as a result, 200 secondary spermatocytes will generate 400 sperms.
Note: Sperm cells are formed during the spermatogenesis process, which occurs in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. This process involves the generation of multiple sperm cell precursors, beginning with spermatogonia and progressing to spermatocytes. The spermatocytes next go through meiosis, which reduces their chromosome number by half and results in spermatids. After that, the spermatids develop and, in animals, build a tail, or flagellum, which gives rise to the mature, motile sperm cell. This entire procedure is ongoing and takes around 3 months from start to end.
