Question
Question: How many \[S{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}0{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}S\] linkages are there in dithionous acid?...
How many S − 0 − S linkages are there in dithionous acid?
Solution
In oxyacid of sulfur, sulfur is the central atom exhibiting a tetrahedral structure when coordinated with oxygen. This contains at least one S=O bond and one S−OH bond. In addition to these, a chain of (−S−)n as in H2S2O6 . Such oxyacids with S−S linkages are called Thioacids.
Complete step by step answer:
The sulfur oxyacids are the acids that contain oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur. These are divided into four groups based on their structural similarities:
1.Sulphurous acid group- these are prepared by dissolving sulphur dioxide in water. Their structure is pyramidal with three oxygen atoms on a triangle i.e. tetrahedral structure is distorted by lone pair. These are strong reducing agents and have bleaching properties.
For example, sulphurous acid H2SO3 .
2.Sulphuric acid group- these are also called oil of vitriol, produced by the lead chamber and contact processes by dissolving SO3 in water. For example, sulphuric acid H2SO4 (oleum) and thiosulphuric acid.
3.Thionic acid group- these are a series of unstable acids with the general formula of H2SnO6 where n = 2 to 6. For example, Dithionic acid H2S2O6 .
4.Peroxo acid group- these are also called Marshall’s acid or Caro’s acid. The central atom sulphur has a +6-oxidation state with a peroxo group in it. These are derived from hydrogen peroxide by replacing hydrogen atoms. For example, peroxydisulfuric acid H2S2O8 .
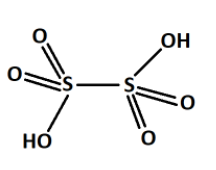
From all these series, we saw that the S−S bond is present only one in the thionic acid series. For example, dithionic acid H2S2O6 . The structure is shown below,
Note: All oxyacids have the acidic hydrogen bonded to an oxygen atom. i.e. −OH bond. The electronegativity of the central atom and the number of O atoms are responsible for the oxyacid acidity.
