Question
Question: How many potential isomers would result in dichlorination of 2, 4-dimethyl pentane?...
How many potential isomers would result in dichlorination of 2, 4-dimethyl pentane?
Solution
The chemical compounds are formed by the difference in the arrangement of the atoms which constitute the compound. Some of the compounds have the same chemical formula but the arrangement of the atoms in the compound is different. These compounds are named isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
The compounds which are different in just the structure but have the same molecular formula are called isomers, some of the isomers can show optical activity, these are called optical isomerism.
When the same compound has a different spatial arrangement in the space, then that is called stereoisomers, while the isomers which only are differentiated with the position of the substituent group are called positional isomers. The positional isomers are the same compounds but the position of the substituents which are attached to the main group will be different in each of the isomeric compounds.
Upon the dichlorination of the compound given, we will get the following products.
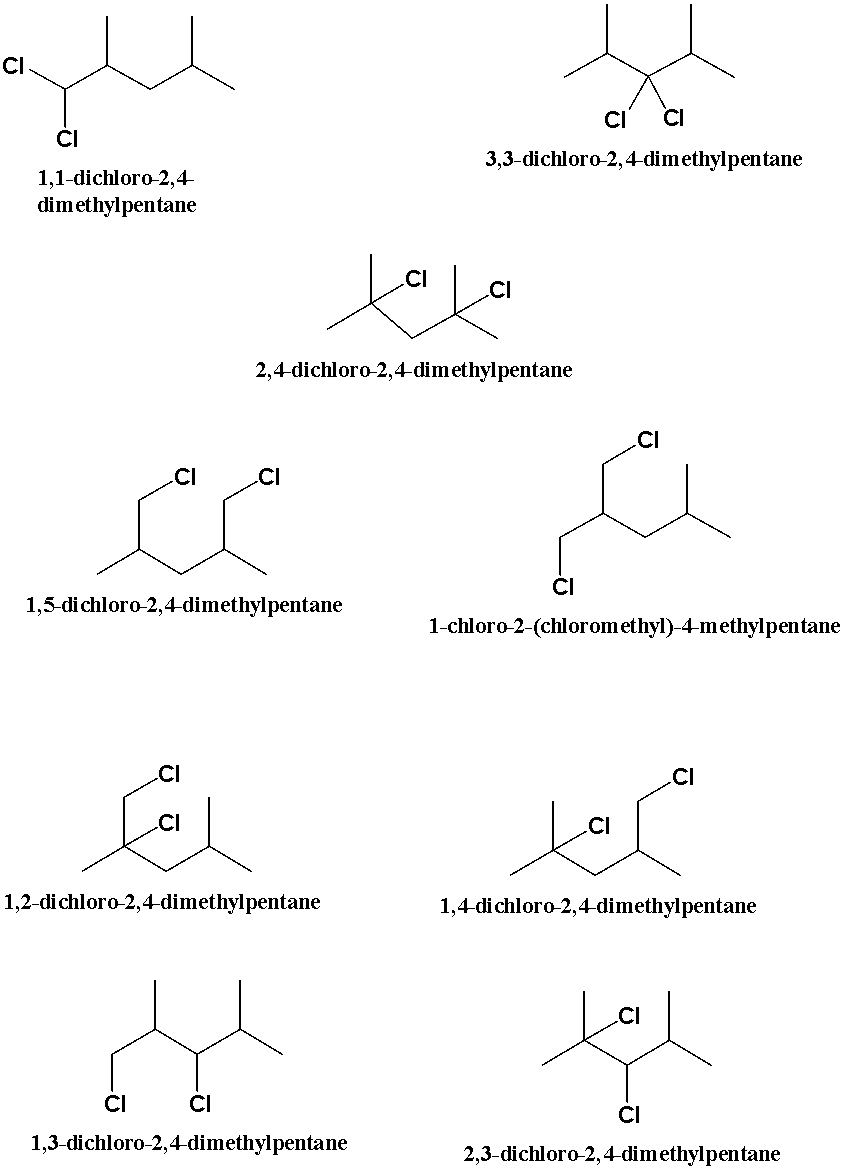
The dichlorination of the 2, 4-dimethyl pentane produces 9 compounds which are seen to be the positional isomers of the di chlorinated compound as the compounds are the potential isomers of the compound since they don’t have the same names but the formula of all the compounds is same.
Note: Carbon is a tetravalent atom which means it has four valence electrons and thus can form four covalent bonds with atoms.
Based on this property the carbon atom can be categorised as primary, secondary or tertiary
The carbon which is attached to only one other carbon atom is called primary carbon, the carbon atom with the attachment of two other carbon atoms is secondary carbon whereas the carbon atom with the attachment of three carbon atoms is termed as a tertiary carbon atom.
