Question
Question: How many \(P - O - P\) bonds(s) is/are present in \({H_6}{P_6}{O_{18}}\) ?...
How many P−O−P bonds(s) is/are present in H6P6O18 ?
Solution
H6P6O18 is known as meta-phosphoric acid. Generally, the number of P - O - P bonds in cyclic metaphosphoric acid is three. P - O - P bonds are the bond linkages present between two phosphorus atoms and one oxygen atom.
Complete step by step answer: The general formula of metaphosphoric acids is (HPO3)n where n denotes the number of phosphoric acid units present in the ring. ‘n’ can be equal to three or greater than three. Metaphosphoric acids have phosphorus in the oxidation state of + 5. It generally decomposes in water and is soluble in alcohol. It is an odorless, glassy substance.
H6P6O18 is meta-phosphoric acid . it is a corrosive inorganic , cyclic polyphosphate formed from bonded phosphoric acid units.
It has applications in biochemistry, agriculture , pharmacy and chemical research.
Structure of meta-phosphoric acid is :
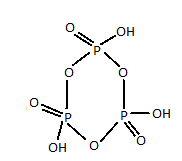
As it is clear from the above representation of meta-phosphoric acid, there are three P−O−P bonds.
So, the answer to the question will be three.
Additional Information:
-Meta-phosphoric acid is used by food analytics to determine the vitamins.
-The biochemistry also makes use of this compound to precipitate protein in biological liquids such as blood and urine.
-For vets, it can be used to check the urea in cattle blood.
-It can also be used as an additive in the production of diagnostic test strips for the pharmaceutical industry.
-Metaphosphoric acid is used to prevent oxidation of reduced glutathione.
Note: Meta-phosphoric acid or H6P6O18 has various uses in various fields. The number of P−O−P bonds in cyclic meta-phosphoric acid is three. Moreover, metaphosphoric acid seems to have some hazardous effects, it can cause burns and may cause injuries to the upper respiratory tract and lungs if inhaled.
