Question
Question: How many lone pair(s) is/are present in the central atom \(I\) of \(I_{3}^{-}\) ion?...
How many lone pair(s) is/are present in the central atom I of I3− ion?
Solution
Think about the number of valence electrons that iodine has and how it hybridizes to form bonds. The hybridization and the valence electrons, along with the number of bonds formed will tell you how many lone pairs exist.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the number of valence electrons in an Iodine atom is 7. Since the charge of the molecule is -1, one more electron is added to the compound. Now the total number of electrons in the compound has become 8. Out of which, two electrons are used to form covalent bonds with two other iodine atoms. Remaining number of electrons that are available is 6. That means, three pairs of electrons. Therefore, the number of lone pairs is 3. The structure of the I3− ion is:
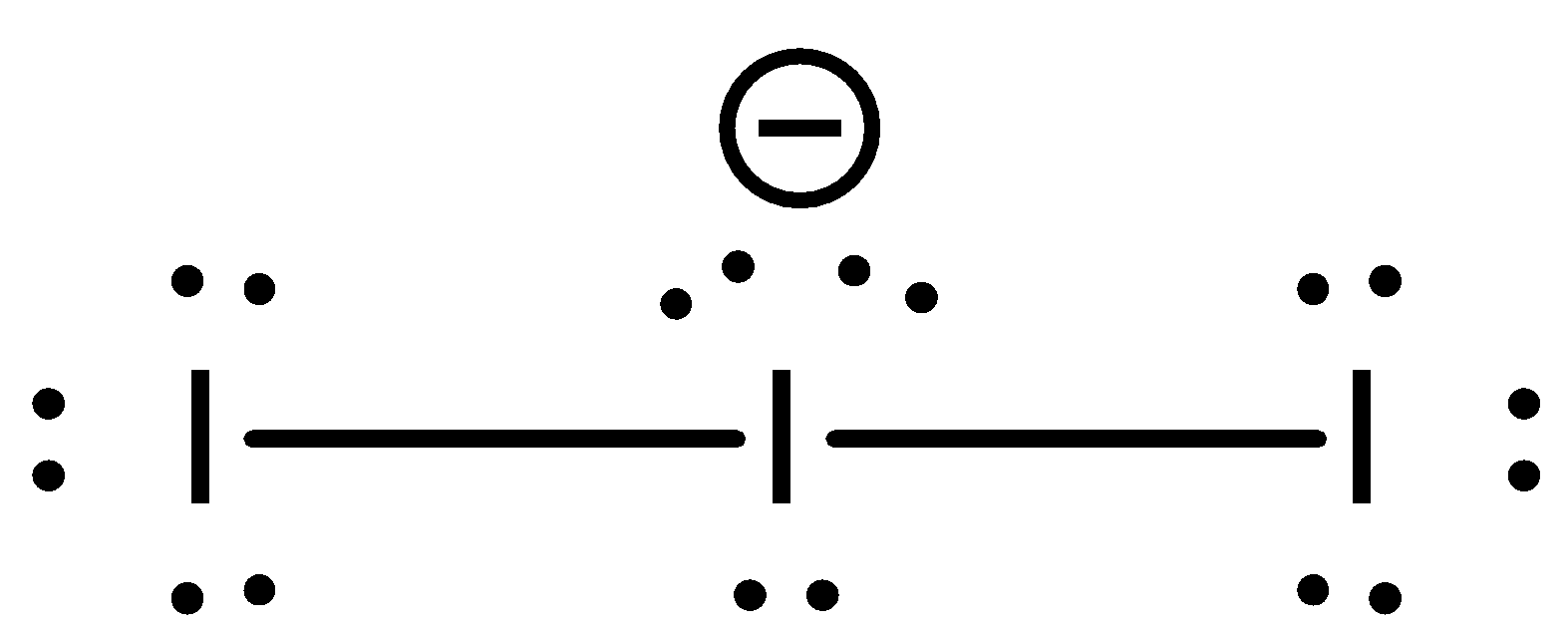
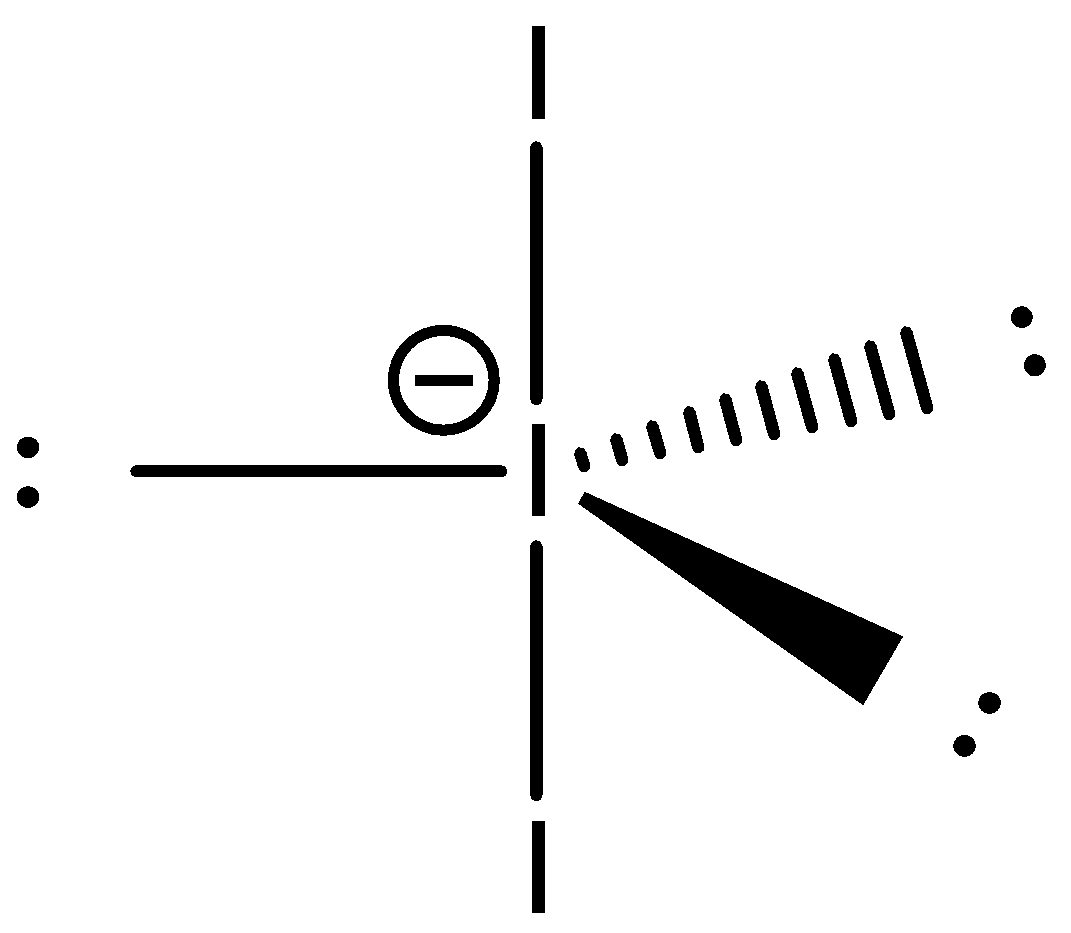
This central atom hybridizes in a trigonal bipyramidal structure. The lone pairs are present at the vertices on the triangle (equatorial) and the iodine atoms are present at the vertices of the pyramids. The hybridized structure of this atom will be:
Additional Information:
- We know that the Iodine atoms in the I3− compound are bonded through covalent bonding. Covalent bonding is the bonding in which mutual sharing of electrons take place.
- Also, the molecular geometry of I3− is linear. While there are three Iodine atoms, one of the atoms has a negative charge which further gives three lone pairs of electrons and two bond pairs. Its steric number is five.
- Here, the name of the compound I3− is Triiodide ion.
- Bond angle of this compound is 180 which means the shape of the molecule is linear.
- Hybridization of this compound is sp3d which shows the electronic geometry is trigonal bipyramidal but the shape is linear since the three equatorial positions are filled with three lone pairs of electrons.
Note: I3− is formed by the bonding of I2 with I− ion. During the combination of Iodine atoms, the central atom gains a negative charge whose value will be 1. I− Ion is the donor and I2 molecule is the acceptor. Electrons are mostly accommodated in the empty d orbitals.
