Question
Question: How many isomers \(x\) of\({C_8}{H_{10}}\) \({C_8}{H_{10}}\) when react with hot alkaline \(KMn{O_4}...
How many isomers x ofC8H10 C8H10 when react with hot alkaline KMnO4 only aromatic dicarboxylic acid? How many isomers y of C4H8 when reacts with hot alkaline KMnO4 given carbon dioxide? Sum of x+y?
Solution
The compounds which exhibit the phenomenon of isomerism are known as isomers. Isomerism is a phenomenon where more than one compound has the same chemical formula but different structures whereas isomers are chemical compounds that have identical chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms in the molecule and also they differ in properties. Also isomerism is of two types’ structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
Complete answer:
Degree of unsaturation, also known as the index of hydrogen deficiency or double bond equivalent, determines the total number of rings and pi bonds in a molecular formula. In terms of degree of unsaturation a saturated molecule only contains a single bond with no rings while unsaturated molecules contain double bond or triple bond and ring.
Degree of unsaturation= [number of carbon atoms +1]-[number of hydrogen atom/2]
So, degree of unsaturation in C8H10=(8+1)−(10÷2) (8+1)−(10÷2)=4
Therefore, a degree of unsaturation of four can contain one ring and 3 double bonds which corresponds to benzene. Hence, 3 isomers are possible so x=3.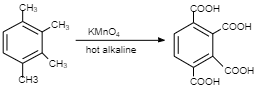
Similarly, degree of unsaturation in C4H8= (4+1)−(8÷2)=1
Therefore, a degree of unsaturation of one can contain a double bond which corresponds to butane. Hence, two isomers are possible so y=2.

So, according to the question:
x+y=3+2
x+y=5
Note:
Hydrocarbons are the compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only and depending on the types of carbon-carbon bonds present, hydrocarbons are classified into three categories which are saturated hydrocarbons, unsaturated hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons which contain only carbon-carbon single bonds while unsaturated hydrocarbons are the hydrocarbons which contain double or triple bonds.
