Question
Question: How many gem dihalides with different formulas are possible \({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}C{{l}_{2}}\)? (a) ...
How many gem dihalides with different formulas are possible C3H6Cl2?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Solution
Hint First of all, write the structural isomer of the given molecular formula and then you will be easily able to know many gem dihalides does this molecular formula will make. But keep in mind that in gem dihalides both the halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we should know what are the gem dihalides. The gem is a prefix and di means two and halides mean halogen. Halides are formed when the halogens gain an electron and acquire the negative charge. So, basically, gem halides are actually those compounds in which the two halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon atom. E.g. like:
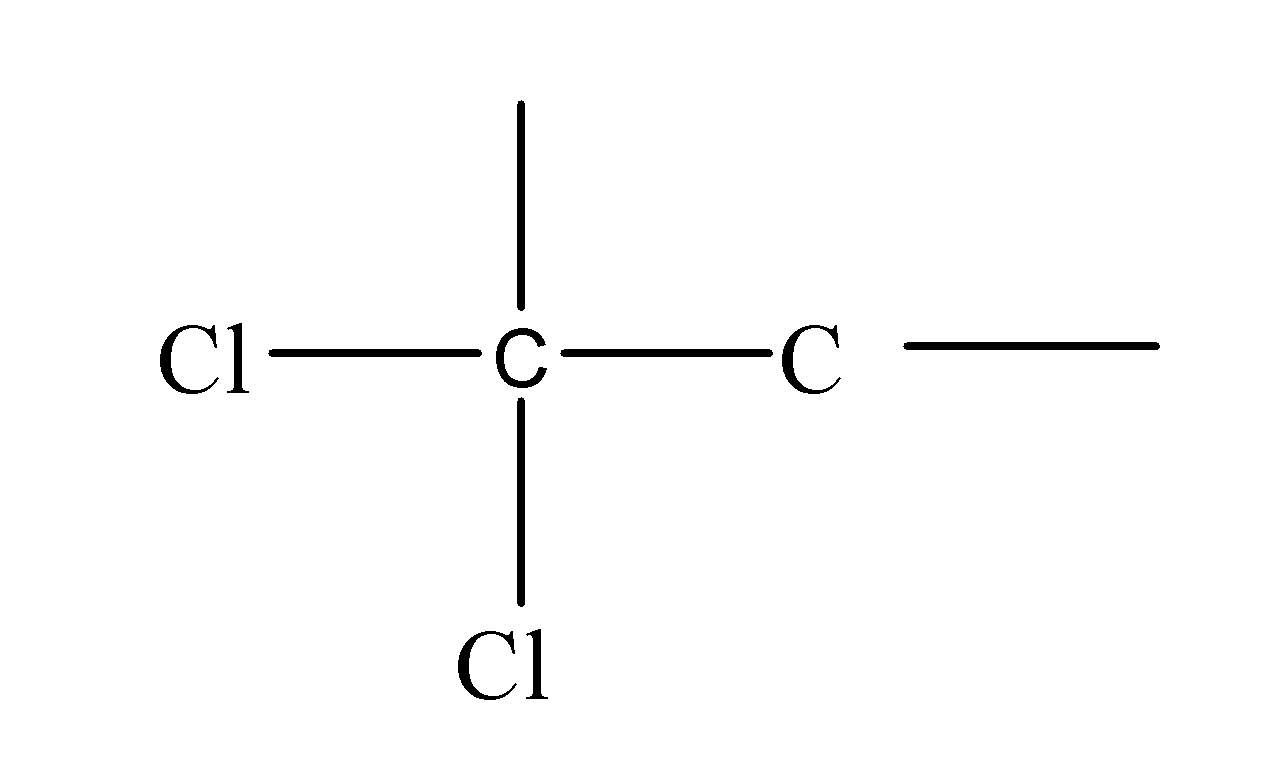
These, halogen atoms can be attached at anywhere along the entire carbon length i.e. can change their position resulting in the formation of different structural isomers( structural isomers are those isomers which have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms along the carbon chain) but the two halogen atoms always form a bond with the same carbon atom though even after changing their positions too along the carbon chain.
Now, we have been given the molecular formula as C3H6Cl2. Now, starting to solve we will first see how many carbon atoms are present in the molecular formula. So, we can see that here three carbon atoms are involved. After that, we will note the number of halogen atoms attached and, in this case, there are two chlorine atoms present. So, it is clear that first the two halogen atoms will get attached to the terminal carbon atom resulting in the formation of an isomer as follows:
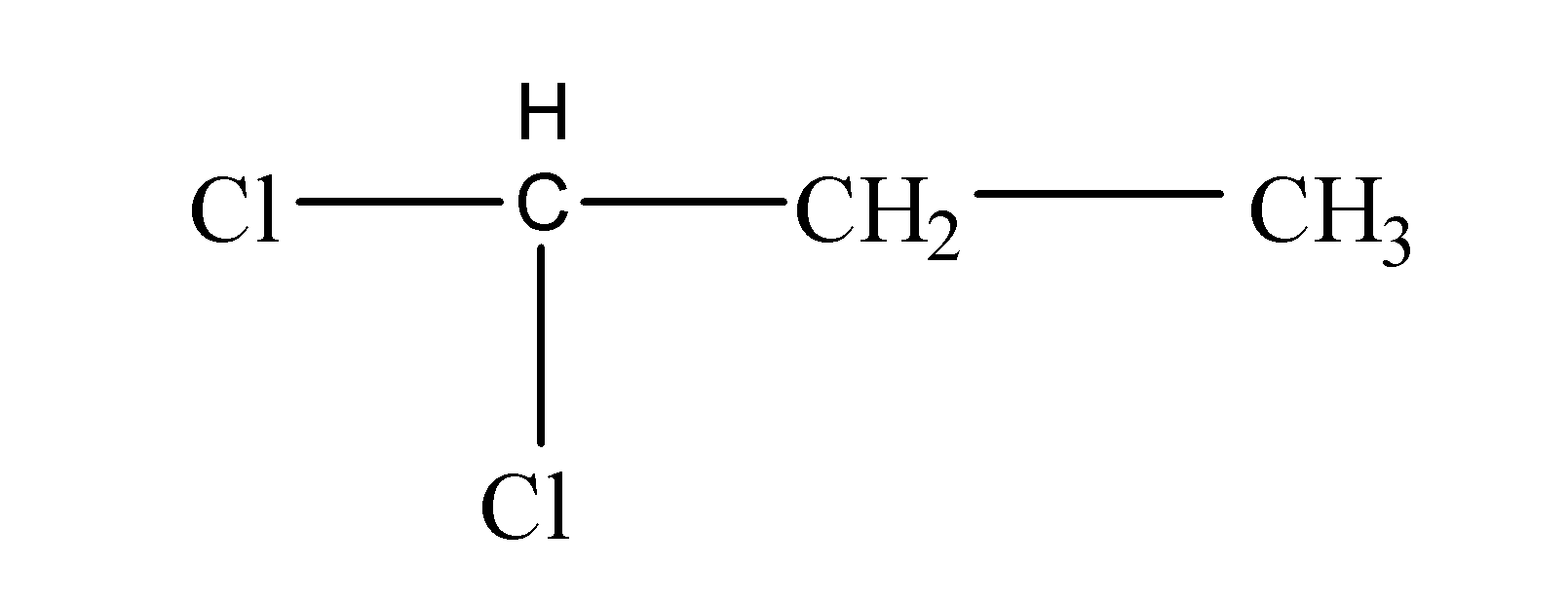
Next, now if we attach the two halogen atoms to the -CH3, then the resulting structure will be same as like the above one because it is also a terminal carbon atom. But if we attach the two halogen atoms to the middle carbon atom, then it would result into the formation of another structural isomer as follows:
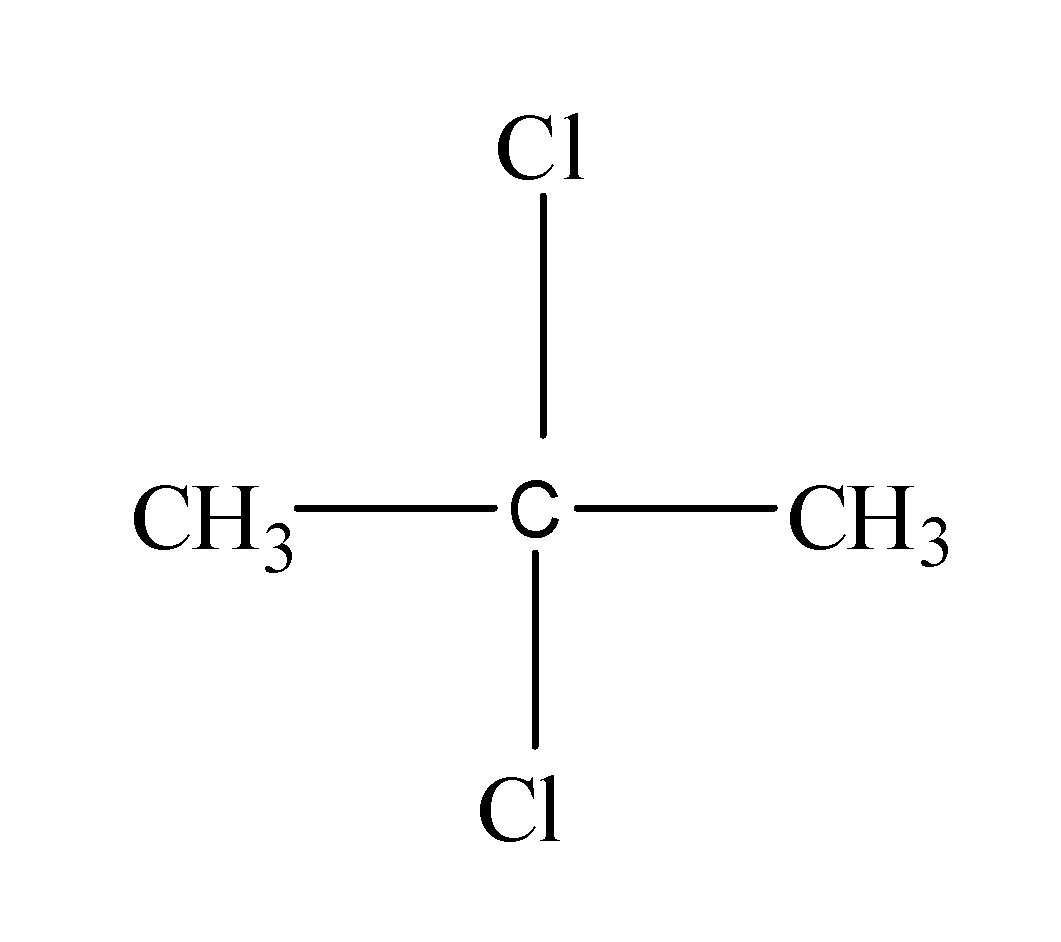
Thus, from the above, it is clear that the C3H6Cl2 forms two different structural formulas.
Hence, option(b)is correct.
Note: Don’t get confused in the gem and vicinal dihalides and read the question carefully. Gem dihalides are attached to the same carbon atom and on the contrary, the vicinal dihalides are attached to the adjacent carbon atom.
