Question
Question: How many different functional groups are present in the given compound? 
A. 6
B. 5
C. 4
D. 3
Solution
In organic chemistry, the functional groups are the substituent groups of atoms which are bonded to the specific molecules. These parts of a molecule are responsible to undergo distinctive chemical reactions and account for the different characteristic chemical properties for those molecules.
Complete answer:
In the given compound, the functional groups present are represented as follows:
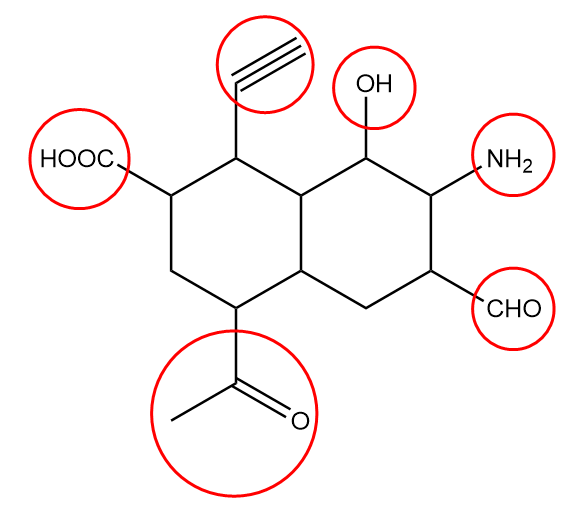
The name and general representation of the functional groups present are as follows:
1. Alcohol: It is generally represented as R−OH, where R represents the rest of the molecule and OH represents a functional group.
2. Amine: It is generally represented as R−NH2, where R represents the rest of the molecule and NH2 represents a functional group.
3. Aldehyde: It is generally represented as R−CHO, where R represents the rest of the molecule and CHO represents the aldehydic functional group.
4. Ketone: It is generally represented as follows:
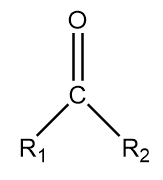
Where, R1 and R2 represent different alkyl groups and −C=O represents ketonic functional groups.
5. Carboxylic acid: It is generally represented as R−COOH, where R represents the alkyl group or the rest of the molecule and COOH represents the functional group.
6. Alkyne: It is generally represented as R1−C≡C−R2, where R1 and R2 represents different alkyl groups and C≡C represents the functional group.
Hence, the total number of functional groups present in the given compound =6. So, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to know that alkanes are not considered as functional groups, in fact an alkane is a compound or a molecule which lacks functional groups due to presence of carbon-carbon single bond which consist of only sigma character that is much stronger and stable than alkenes and alkynes.
