Question
Question: How many Cl−Cl bond(s) is/are present in \( C{l_2}{O_7} \)...
How many Cl−Cl bond(s) is/are present in Cl2O7
Solution
Hint : A chemical bond is a long-term attraction between atoms, ions, or molecules that allows chemical compounds to form. Ionic bonds are formed by the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions, whereas covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons. Chemical bonds come in a variety of strengths; there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" like covalent, ionic, and metallic connections, as well as "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" like dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force, and hydrogen bonding.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The chemical compound Cl2O7 stands for dichlorine heptoxide. The anhydride of perchloric acid is chlorine oxide. Perchloric acid is carefully distilled in the presence of the dehydrating agent phosphorus pentoxide to create it:
2 HClO4+ P4O10→ Cl2O7+ H2P4O11
The chlorine(VII) oxide in the mixture may be distilled off. Illumination on chlorine and ozone mixes can also produce it. When anhydrous, it slowly hydrolyzes back to perchloric acid, which is similarly dangerous. Cl2O7 is an endergonic molecule, which means it's intrinsically unstable and breaks down into its constituent atoms when energy is released. Cl2O7 is bent at 118.6o with the Cl−O−Cl angle, producing the molecule C2 symmetry. The terminal Cl=O distances are 1.709 , while the Cl=O distances are 1.405 . Although the bonding in this molecule is largely covalent, chlorine lives at its maximum formal oxidation state of +7 in this chemical.
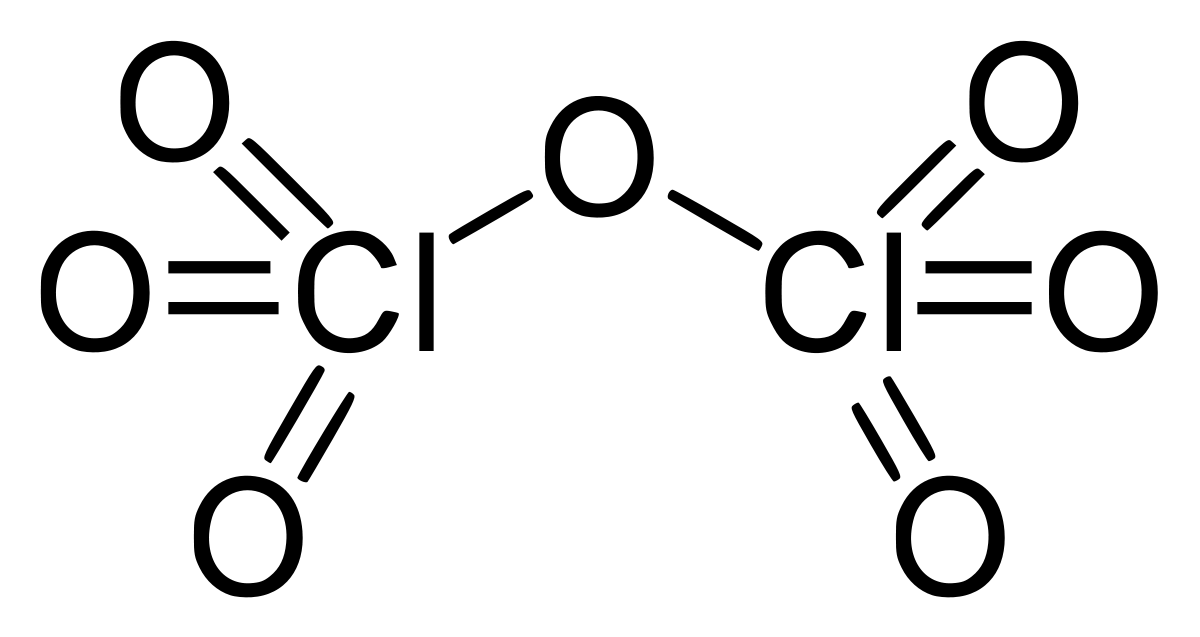
here no two chlorines are getting attached.
Hence the answer is zero.
Note :
Cl2O7 , although being the most stable chlorine oxide, is a powerful oxidant and explosive that may be ignited by flame, mechanical force, or contact with iodine. It is, however, less oxidising than the other chlorine oxides, and when cold, it does not damage sulphur, phosphorus, or paper. It has the same effects on the human body as elemental chlorine and must be handled with the same care.
