Question
Question: how many aldehydes are possible with molecular formula \({{C}_{4}}{{H}_{8}}O\) ? A.\(1\) B.\(2\...
how many aldehydes are possible with molecular formula C4H8O ?
A.1
B.2
C.3
D.4
Solution
An aldehyde is defined as a functional group that consists of a carbonyl centre with carbon atoms that are also bonded to the hydrogen and R group. R group can be a hydrogen, alkyl group or any side chain. Molecular formula consists of atoms that have some numeric value as a subscript that tells us about the number of atoms present.
Complete answer:
Molecular formula is defined as the formula that contains chemical symbols of the elements having some numerical subscripts that describes the presence of a number of atoms in a molecule. The limitation of molecular formula is that they are not able to describe the arrangement of the atoms in a molecule. Structural formula is different from molecular formula as it is helpful in describing the number of atoms as well as the arrangement of the atoms in a molecule. In organic compounds, carbon and hydrogen are the first elements in the molecular formula.
Now let us see the structure of the two aldehydes.
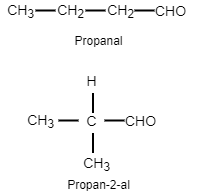
We have seen that two aldehydes are possible with the molecular formula C4H8O
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Additional information:
A chemical formula is defined as a way of representing the chemical proportions of the atoms that combines together to form a molecule.
Empirical formulas are the simplest type of chemical formula that just only requires numbers and alphabets. Empirical formulas do not contain large numbers. For example, the empirical formula for glucose is CH2O and molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6
Note: Isomers are defined as the compound having the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms. In this question, C4H8O are the aldehydes that can be arranged in different forms. This process is known as isomerisation. It is not necessary that the isomers will share the same chemical properties as physical properties.
