Question
Question: How is mitosis different in plant and animal cells?...
How is mitosis different in plant and animal cells?
Solution
Mitosis is a type of cell division which is also known as the equational division as there is no change in the number of chromosomes before and after the division takes place. It takes place in both somatic cells as well as gametangial cells.
Complete Answer:
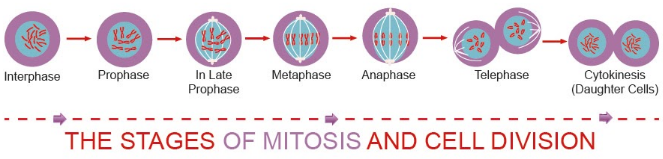
The process of mitosis results in the formation of two daughter cells which are genetically identical and takes place through karyokinesis and cytokinesis. Mitosis is different in plant and animal cells by the way cytokinesis takes place in them. In animals, cytokinesis takes place through the formation of a furrow in the plasma membrane whereas, in the case of plants, cytokinesis takes place through the formation of a cell wall. The cell furrow is formed by the flexible plasma membrane which deepens with time until it joins in the center resulting in the division of the cell. In the case of the cell wall, it is formed in the center of the cell and grows outwards to meet the lateral walls to divide the cell.
Additional information:
-The precursor of the cell wall is known as the cell plate which later forms the middle lamella between two cells.
-The growth of cell furrow is centripetal (inwards) whereas the growth of the cell wall is centrifugal (outwards) in nature.
-Mitosis takes place in living beings for the purpose of growth, cell repair, and replacement of old cells.
-Mitosis also takes place to restore the nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio which was disturbed due to the growth of the cell.
Note:
-When karyokinesis is not followed by the process of cytokinesis, it results in the formation of a multinucleate condition as seen in the liquid endosperm of coconuts.
-Karyokinesis is further divided into four stages known as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
-During cytokinesis, cell organelles are distributed into the daughter cells along with the divided nucleus.