Question
Question: How is benzamide obtained from benzoic acid?...
How is benzamide obtained from benzoic acid?
Solution
Hint: To draw the conversion of benzoic acid to benzamide we should know about the conditions that are required for production of benzamide. We should know that in benzamide it has an amine group attached to it.
Step by step answer:
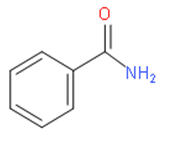
Before drawing the conversion of benzoic acid to benzamide, we should know about benzamide. We should note that benzamide is a white solid with the chemical formula of C6H5C(O)NH2. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid.
It has the following structure:
For the synthesis of benzamide from benzoic acid, we should use thionyl chloride (SOCl2)
with benzoic acid to convert it in benzyl chloride. In this reaction, we will replace OH to Cl then we
will use NH3 which upon reacting with benzyl chloride will give us benzamide. This
reaction will be as follows:
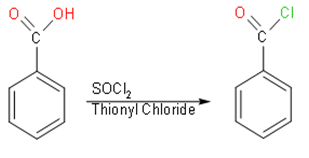
So, in the above reaction we had converted benzoic acid to benzoyl chloride. We should note that benzoyl chloride appears as a colourless fuming liquid with a pungent odour. We should note that benzoyl chloride is a typical acyl chloride. It reacts with alcohols to give the corresponding esters.
Similarly, it reacts with amines to give the amide. So, if we react with benzoyl chloride with amines it will give amide. We should know that we use thionyl chloride, because it is used as a chlorinating agent.
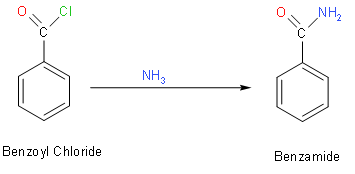
So, in the above reaction we had converted benzoic acid to benzamide.
Note: We can also prepare benzamide with the help of benzonitrile. When benzonitrile is mixed with sulphuric acid, a clear solution is rapidly obtained. We should then heat it for 20 minutes. When the hydrolysis reaction is complete the solution is cooled. The obtained precipitate is of crude benzamide.We should be extremely careful while making benzamide from thionyl chloride, because it is highly corrosive and toxic. Long-term inhalation of low concentrations or short-term inhalation of high concentrations has adverse health effects.
