Question
Question: How does the resistance affect the current in a circuit?...
How does the resistance affect the current in a circuit?
Solution
Current in a circuit flows from one point to the other when there exists a potential difference between the points. Resistance opposes the flow of current. The relationship between potential difference, current and resistance of a circuit is given by the ohm’s law. At constant voltage, we can determine the relation between current and resistance.
Complete answer:
The resistance is the property of a material by virtue of which it resists the flow of current through it. Its SI unit is ohms (Ω). In a circuit the resistance is provided by resistors. Resistors can be connected in series or parallel in a circuit.
According to the ohm's law,
R=IV
Here, R is the resistance
V is the potential difference across a circuit
I is the current in the circuit
From the above equation we can see that current is inversely proportional to the resistance in the circuit. Therefore,
R∝I1
This means as the resistance increases, the current decreases and vice versa. The graph between current and resistance is shown in the figure below
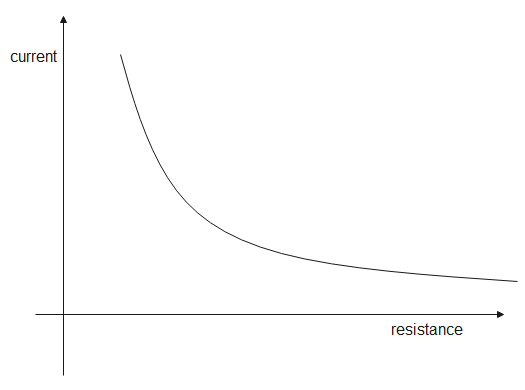
The graph shows the inverse relation between current and resistance. The slope of the graph will be negative.
Therefore, current is inversely proportional to the resistance; current decreases with increase in resistance and vice versa.
Note:
The relationship between current and resistance is true when the potential difference is constant. The resistance depends on the temperature and nature of material. The insulators have the highest resistance, semiconductors have a lower resistance and the conductors have the lowest resistance. With increase in temperature, the resistance of insulators and semiconductors decreases but the resistance of conductors increases.
