Question
Question: How does the Mitochondria make energy?...
How does the Mitochondria make energy?
Solution
An organelle is a subcellular structure that, like an organ in the body, has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell. The nuclei, which store genetic information, mitochondria, which produce chemical energy, and ribosomes, which assemble proteins, are among the most important cell organelles.
Complete answer:
In most eukaryotic organisms, a mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound organelle. Mitochondria produce the majority of the cell's adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used as a chemical energy source. Kolliker (1880 CE) discovered mitochondria in the voluntary muscles of insects for the first time.
Some multicellular organisms' cells lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). Microsporidia, parabasalids, and diplomonads are among the unicellular organisms that have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures.
Mitochondria are known as the cell's powerhouse because they are in charge of extracting energy from food via cellular respiration. Adenosine triphosphate is used to release the energy (ATP). It is the cell's energy currency. Below is a diagram of Mitochondria's structure.
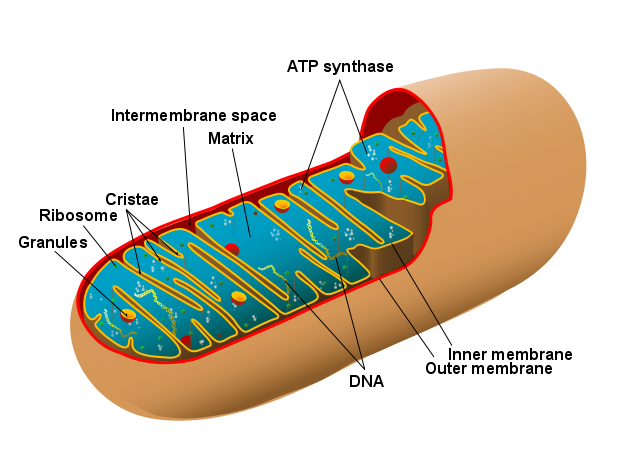
Thus, Mitochondria produce energy as part of the cellular respiration process. Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles found in all eukaryotic cells' cytoplasms. Through cellular respiration, they extract energy from food in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). Mitochondria produce energy (ATP) molecules in the cell by oxidizing glucose's major products with the help of specific proteins and enzymes. Therefore, mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell.
Note:
The number of mitochondria in a cell varies dramatically depending on the organism, tissue, and cell type. A mature red blood cell has no mitochondria, whereas a liver cell can have up to 2000 mitochondria. The mitochondrion is divided into compartments that each perform a specific function. The outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix are examples of compartments or regions.
