Question
Question: How does one tell if a compound is optically active or inactive by looking at it? For example : 1,4-...
How does one tell if a compound is optically active or inactive by looking at it? For example : 1,4-dichloro-2-methylpentane and 1,2-dichloro-2-methyl pentane.
Solution
The optically active compounds are those which can rotate the plane polarized light. All chirals compounds have the capability of optical rotation. The chiral compounds are those where the carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or groups.
Complete step by step answer:
The compounds which are capable of optical rotation are said to be optically active compounds. All the chiral compounds are optically active.
The chiral compound contains an asymmetric center where the carbon is attached with four different atoms or groups. It forms two non-superimposable mirror images.
The structure of 1,4-dichloro-2-methylpentane is shown below.
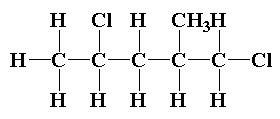
In 1,4-dichloro-2-methylpentane, two chiral carbons are present. The C2 carbon and C4 carbon are the chiral carbon present which are attached with four different groups.
The C2 carbon is attached to H, CH3, CH2Cland CH2CHClCH3.
The C4 carbon is attached to H, Cl, CH3 and CH2CH(CH3)CH2Cl.
So, the compound 1,4-dichloro-2-methylpentane is optically active in nature.
The structure of 1,2-dichloro-2-methylpentane is shown below.
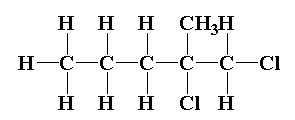
In 1,2-dichloro-2-methylpentane C2 carbon is the chiral carbon.
The C2 carbon is attached to four different atoms or groups.
The C2 carbon is attached to CH3, Cl, CH2Cl and CH2CH2CH3.
So, the compound 1,2-dichloro-2-methylpentane is optically active in nature.
Note:
When two non-superimposable mirror images are formed by the chiral compounds, then the compounds are said as enantiomers of each other. They are mirror images of each other.
