Question
Question: How does \[{H_2}{O_2}\] react within the acidic medium in either cold conditions?...
How does H2O2 react within the acidic medium in either cold conditions?
Solution
To solve the question we can react hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7). After the reaction, we can observe some changes under the suitable conditions of the reaction. Here we will react the reactants hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) in an acidic medium.
Complete answer:
First, we will write the properly balanced reaction of the given reactants under the given conditions. So here the reactants are hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7). We need to react to the reactants in the presence of an acidic medium. We are considering acidic medium as sulphuric acid (H2SO4) in cold conditions. Now the reaction can be written as, 4H2O2+K2Cr2O7+H2SO4→2CrO5+K2SO4+5H2O
From the above-balanced chemical reaction, we can observe that when hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) reacts in the acidic medium the major product formed is chromic acid (CrO5) with potassium sulfate and water. The presence of chromic acid (CrO5) is the blue-colored formed acid.
Additional Details:
Other than this we can explore the structure of the major product chromic acid (CrO5) formed. The structure of chromic acid is represented as 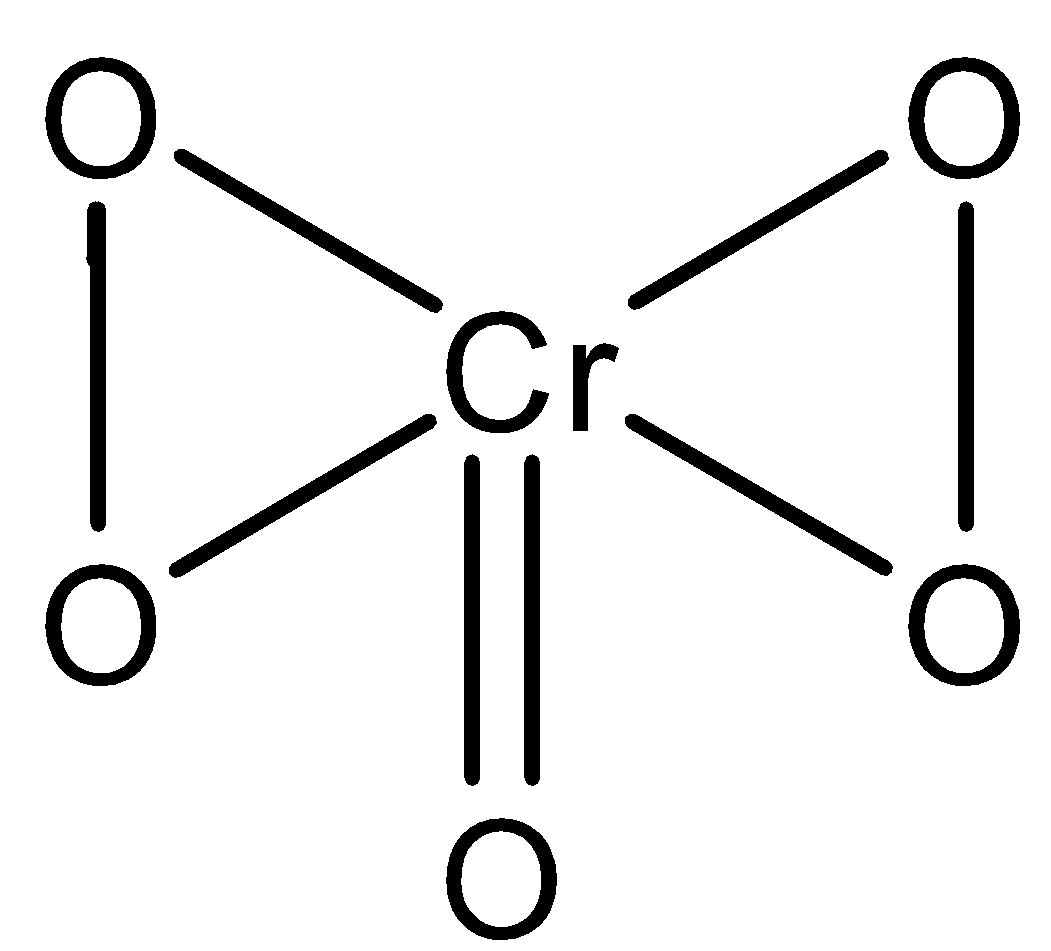 .
.
-By observing the structure we can note that four oxygen atoms are linked to the central atom by peroxide linkages. We can also calculate the oxidation state of chromic acid if we know the oxidation states of other oxygen atoms. The four oxygen are linked by peroxide linkage. Therefore, the oxidation state of the four oxygens will be −1. The other oxygen atom is in −2 an oxidation state. Therefore, the oxidation state Cr is x+4×(−1)+(−2)=0,x=6.
Note:
Chromic acid is commonly known as chromium peroxide. The structure of chromic acid (CrO5) is like a butterfly. In cold conditions, chromic acid is stabilized by the ice-cold ether. There are 4 peroxy-linkages in chromic acid.
