Question
Question: How does freezing point depression occur?...
How does freezing point depression occur?
Solution
Freezing point is the point at which matter changes its state from liquid to solid and vice versa, Upon addition of non-volatile solute in a pure liquid we observe that the freezing point of the pure liquid falls to a lower value
Complete step by step answer:
All the colligative properties are the resultant of lowering of chemical potential upon addition of a solute, chemical potential of a substance in itself is proportional or related to the vapor pressure of a substance thus we can understand this phenomenon better by using vapor pressure which is an easier to understand term.
Vapor pressure is the measure of tendency of substances to go into the gaseous or vapor state. i.e. it now freezes at a temperature lower than it’s freezing point this is what is known as Depression in freezing point. It is a colligative property i.e. the more the number of particles of non-volatile solute the greater will be its magnitude.
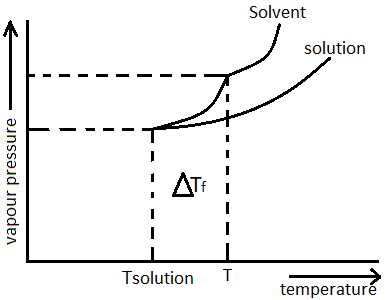
Initially the solid state and liquid state of a pure solvent exists in equilibrium and this equilibrium has a certain vapor pressure associated with it, upon addition of an external non-volatile solute the vapor pressure value falls and thus the solid solution now reaches equilibrium with the liquid solution at a temperature lower than what it did as in pure solvent state.
This is how freezing point depression occurs.
Note: Note that the special take home point here is the fact addition of any non-volatile substance would bring in the same amount of lowering in freezing amount if given in equal amounts thus it does not matter what solute we use until and unless it is non-volatile. If however a solute more volatile than the solvent is added then what we see is an elevation in freezing point rather than depression.
