Question
Question: How does DNA change to mRNA?...
How does DNA change to mRNA?
Solution
The first step of gene expression, where a DNA sequence is read by various enzymes and is converted to RNA which will later be decoded and translated into proteins. In the case of eukaryotes, this process is very complex.
Complete answer:
Transcription is the first step of gene expression in living organisms where the DNA is copied and transcribed into RNA to be further translated into proteins.
- The process of transcription starts by binding the RNA polymerase to the promoter, the promoter is an upstream sequence of DNA in the gene.
- The sequences of DNA that are responsible for sending the signals at the binding site for the process of transcription to start by the initiation of transcription factors along with RNA Polymerase.
- Promoters are upstream sequences present in the starting base pairs of gene around 100-1000 base pairs long in DNA that helps in the starting of the process of transcription.
- RNA Polymerase produces RNA from DNA that either codes for proteins in the form of messenger RNA or non-coding RNA that function as enzymes or regulate other processes.
The process occurs in three main steps:
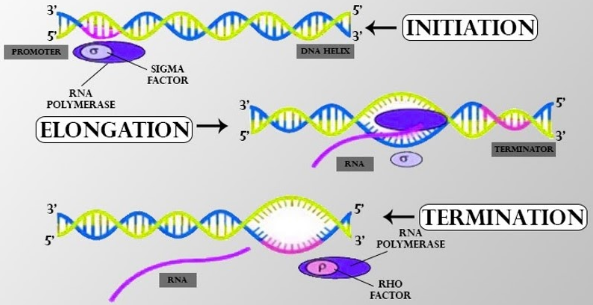
Initiation – In this step, the double helix DNA strand is unwounded and becomes single-stranded near the initiation site. The promoter sequence is called a Pribnow box / TATA box that binds itself to for the initiation of the process of transcription of the single-stranded DNA. To bind the promoter with the RNA polymerase enzyme the sigma factors are required.
Elongation – The sigma factor stops and removes itself from the promoter after it has synthesized more than 10 base pairs of long RNA. The RNA polymerase enzyme then moves in the 5’ – 3’ direction continuously all the while synthesizing RNA.
Termination – The last step of transcription is termination. It has two types of mechanisms-
-Rho-independent transcription termination – transcription is terminated due to a specific sequence in terminator DNA. This terminator DNA forms transcript RNA from the hairpin structure that contains invert repeats resulting in the complementary pairing. This leads to the removal of RNA polymerase from the template of DNA.
-Rho-dependent transcription termination – here with the help of rho protein the process of transcription is stopped. It then attaches to RNA during transcription. It later detaches itself from RNA polymerase from DNA.
Note:
Bacterial transcription differs from eukaryotic transcription, as in bacteria transcription and translation both can occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm of the cell whereas in eukaryotes transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. RNA polymerase enzyme is of a single type in case of Bacteria while it is of three types in the case of eukaryotes.
