Question
Question: How does benzene differ from hexane?...
How does benzene differ from hexane?
Solution
First we need to have an idea about hydrocarbons and its structures. It is evident that benzene and hexane are hydrocarbons in nature but they are different in structure and general formula. Therefore we should have a clear idea on its structure and general formula to substantiate the difference between both. Here we need to know benzene is an aromatic compound whereas hexane is an aliphatic compound.
Complete answer:
First we shall look into the case of benzene.
Let us consider a class of hydrocarbons where molecular formulas are the same as that of unsaturated hydrocarbons but the main thing to notice here is they do not undergo additional reactions unlike alkenes. Such compounds are placed in a distinct class known as aromatic hydrocarbons. It is also having unique structure and properties. One of such simplest compounds is benzene, having formula C6H6 .
C6H6 formula of benzene indicates its high degree of unsaturation . Benzene is having four degrees of unsaturation. Here another point is each degree of unsaturation implies C=C junction as in ethylene or ring junction. Benzene is an aromatic compound which is constrained in a ring structure. The ring structure of benzene comprises alternate single and double bonds. Benzene is having structure as below,
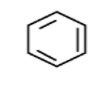
Next we have to look onto alkane. Alkane has a general formula CnH2n+2 which is fully saturated . In this , each two hydrogen less than this formula specifies one degree of saturation. Here the hexane comes under this alkane group.
Hexane is an aliphatic compound which is not constrained in a ring. Hexane contains eight more hydrogen atoms than benzene in which the former is having the general formula C6H14 . It has only single bonds that link C atoms to group together as well as C atoms to attach with hydrogen atoms. Hexane is having structure as below,
CH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH3
Note: We know benzene is an aromatic compound which is unsaturated. Due to this consequence of unsaturation, benzene can undergo aromatic electrophilic substitution. Hexane is an organic compound containing five isomeric aliphatic hydrocarbons which are colourless in nature and are volatile liquids. Also , an important point is that an unsaturated compound is also a saturated compound , which contains double or triple bonds but not having single bonds.
