Question
Question: How does a covalent bond become polar?...
How does a covalent bond become polar?
Solution
A chemical bond is defined as a lasting interaction between atoms which leads to the formation of chemical compounds. The type of interactions present are used to define the nature of bonds into Ionic and Covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are bonds formed between atoms via sharing up of their electrons in an even or uneven fashion whereas ionic bonds are formed between atoms due to electrostatic interactions.
Complete step by step answer:
The general notion that we have about covalent bonds is that they are formed by sharing of electrons between two or more atoms. However what we fail to conceive from this definition is the fact that it never specifies about which atoms should donate more or donate less or even donate electrons at all.
This is where the term Electronegativity comes in. Due to difference in electronegativity of atoms in heteroatomic molecules the shared pair of electrons are generally closer to one of the atoms in a bond, this leads to the generation of polar character in a covalent bond. So in short a covalent bond becomes polar when it is formed between atoms having different electronegativity. To understand this better, let us consider two different cases:
1)
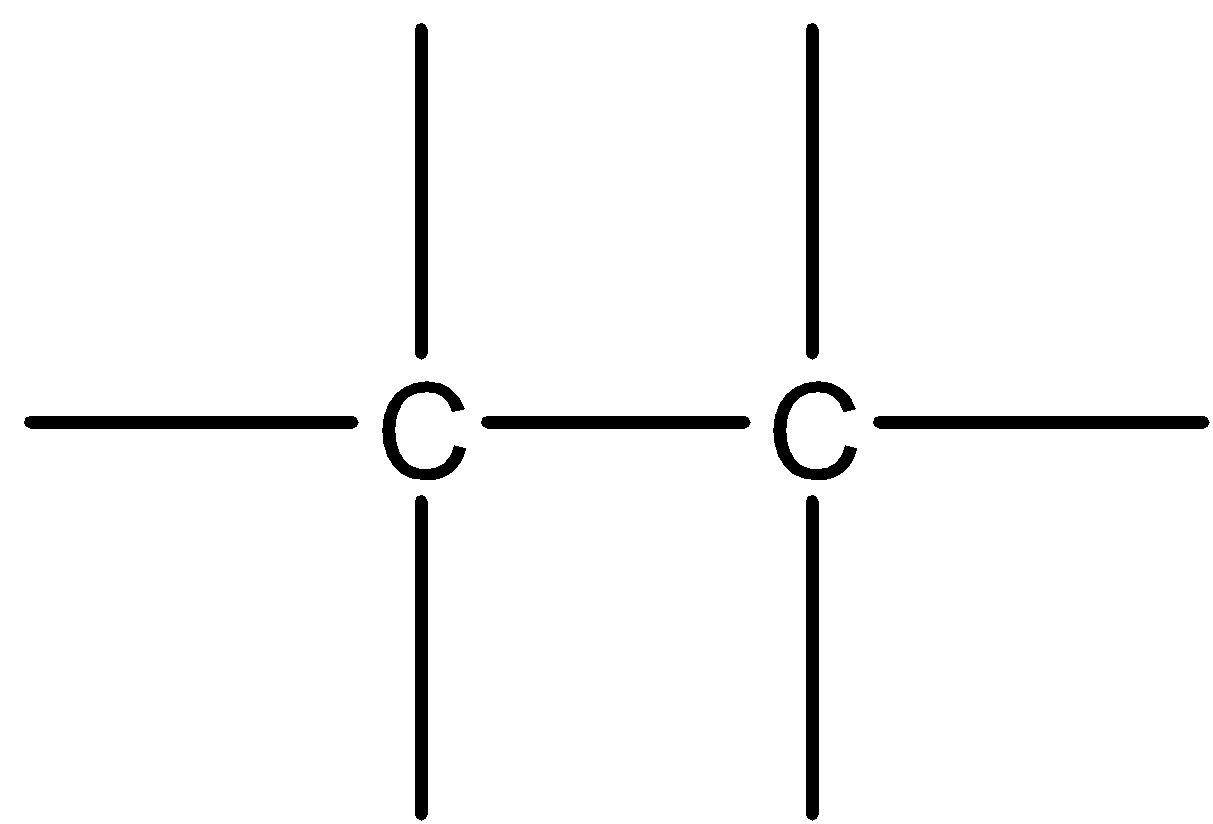
In this compound, both atoms of carbon possess the same electronegativity. Hence, they share the electrons of covalent bonds equally. As a result, it is a nonpolar covalent bond.
2)
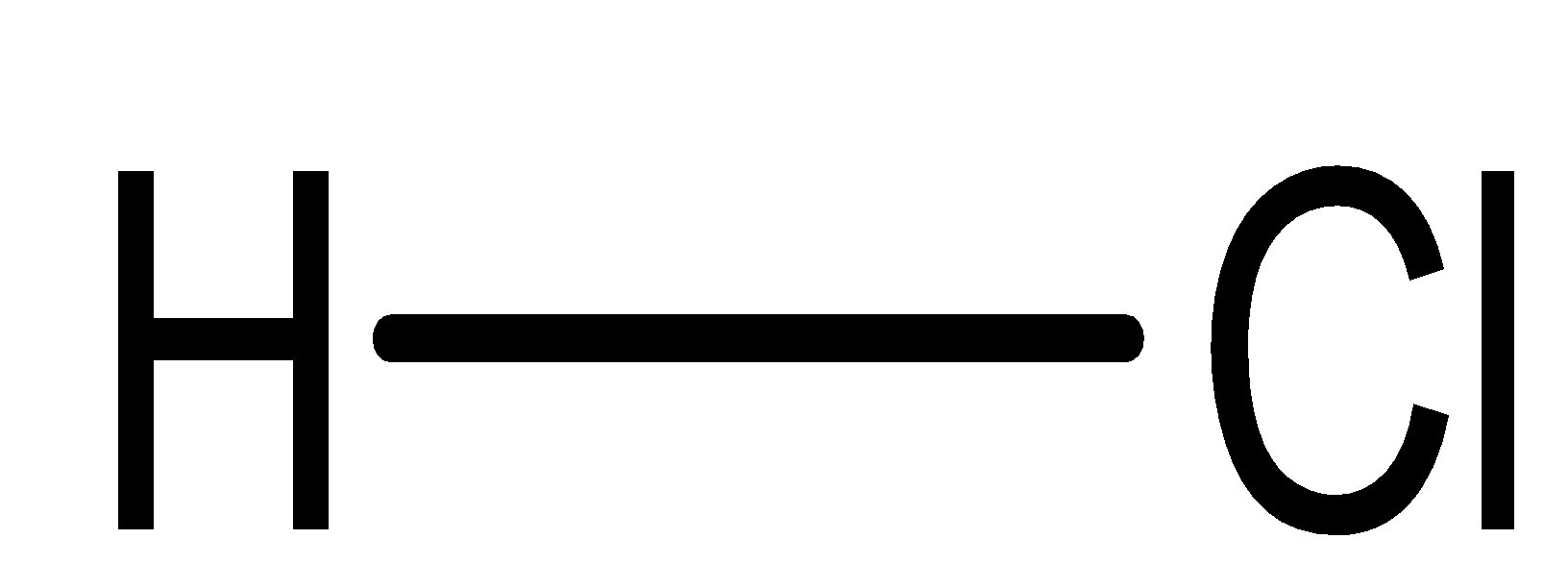
In this compound, one atom is hydrogen while the other is chlorine. We know that chlorine is more electronegative and possesses the tendency to draw a shared pair of electrons towards itself. Hence, it creates polarity. As a result of unequal sharing of electrons (or difference in electronegativity), it is a polar covalent bond.
Additional Information:
Electronegativity is the property of atoms to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself. It is measured via various scales like Allred-Roschow, Mulliken and Pauling wherein the Pauling scale is the most practical and commonly used one where Fluorine atom is taken as the reference for defining the scale.
Note: Always try to think broadly when you hear the word covalent bond as it can be of two types either polar covalent bond or nonpolar covalent bonds thus depending on which type of covalent bond you are dealing with we can always say that it may contain polar character.
