Question
Question: How does a bridge circuit work?...
How does a bridge circuit work?
Solution
Bridge circuits work on the null balance meter comparing two voltages. A third branch connected between the two circuit branches in a point between them. A galvanometer is connected and current flows through it in unbalanced condition and in balance condition no current flows through it.
Complete answer:
The bridge circuit was constructed in earlier days to calculate the values of unknown resistances but now it can be done with some advanced modern techniques.
Bridge circuit is constructed with a series and parallel combinations of four resistances in a circuit in a shape of diamond as shown in figure.
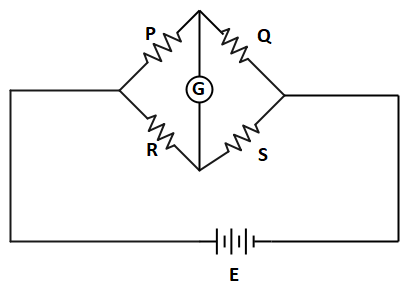
To calculate an unknown resistance with a wheatstone bridge we need two known resistors, one unknown resistor and one variable resistor whose value can be changed according to our need. When the current in the galvanometer becomes zero and the bridge is balanced the ratio of two known resistors to the ratio of variable and unknown resistor will be equal and the value of unknown resistor can easily be calculated.
If a galvanometer is not present then this circuit can be considered as voltage divider circuit normally as other circuits. Resistance measurement via bridge circuit can be done from high resistance (mega ohms) to low resistance (Milliohms or micro ohms).
Note:
Bridge circuits can be useful for measuring unknown resistance precisely, they can be used with amplifiers to measure strain, temperature etc. or can be used with capacitance or inductance with many types of variations in it. The fractional measurement of resistance in a bridge circuit is mostly used in thermometer measurements.
