Question
Question: How do you write the balanced chemical equation for the acid hydrolysis of methyl butanoate?...
How do you write the balanced chemical equation for the acid hydrolysis of methyl butanoate?
Solution
balancing chemical equations involves the addition of stoichiometric coefficient to the reactant and products. This is important because a chemical equation must obey the law of conservation of mass and the law of constant proportions, i.e. , the same number of atoms of each element must exist on the reactant side and the product side of the equation.
When we say about the acid hydrolysis of an ester, we just mean adding water to that Easter (using an acid catalyst) and breaking the ester bond (COO) to form an alcohol and carboxylic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Acidic or alkaline hydrolysis of esters yields a carboxylic acid and alcohol.
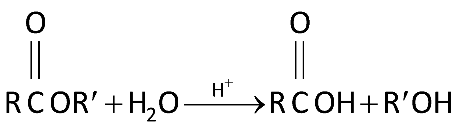
In this reaction we are adding water to ester and using acid as a catalyst. And breaking the ester bond (COO)to form an alcohol and carboxylic acid.
This reaction can be a reverse of water condensation where it involves ejection of a water molecule when two molecules form together to form a larger molecule. This is what happens when esters are hydrolysed by dilute acid such as dilute hydrochloric acid and water.
In writing a balanced chemical equation make sure that atoms on the reactant side and product side are equal.
When acid hydrolysis of methyl butanoate is performed what we will get
C3H7COOCH3+H2O/H+→C3H7COOH+CH3OH
This the balanced chemical equation of acid hydrolysis of methyl butanoate. It will give botanic acid and methanol as products.
Note: The protonation of ester makes carbon more reactive for nucleophilic attack. Hence a Reversible reaction.
While writing any equation just make sure the number of atoms are equal on both the sides. And if they are not balanced it should be done by different methods of balancing. And always remember the law of conservation of matter.
